Roles of regulatory T cells in cancer immunity
- PMID: 27160722
- PMCID: PMC4986235
- DOI: 10.1093/intimm/dxw025
Roles of regulatory T cells in cancer immunity
Abstract
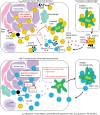
CD4(+) regulatory T cells (Tregs) expressing the transcription factor FoxP3 are highly immune suppressive and play central roles in the maintenance of self-tolerance and immune homeostasis, yet in malignant tumors they promote tumor progression by suppressing effective antitumor immunity. Indeed, higher infiltration by Tregs is observed in tumor tissues, and their depletion augments antitumor immune responses in animal models. Additionally, increased numbers of Tregs and, in particular, decreased ratios of CD8(+) T cells to Tregs among tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are correlated with poor prognosis in various types of human cancers. The recent success of cancer immunotherapy represented by immune checkpoint blockade has provided a new insight in cancer treatment, yet more than half of the treated patients did not experience clinical benefits. Identifying biomarkers that predict clinical responses and developing novel immunotherapies are therefore urgently required. Cancer patients whose tumors contain a large number of neoantigens stemming from gene mutations, which have not been previously recognized by the immune system, provoke strong antitumor T-cell responses associated with clinical responses following immune checkpoint blockade, depending on the resistance to Treg-mediated suppression. Thus, integration of a strategy restricting Treg-mediated immune suppression may expand the therapeutic spectrum of cancer immunotherapy towards patients with a lower number of neoantigens. In this review, we address the current understanding of Treg-mediated immune suppressive mechanisms in cancer, the involvement of Tregs in cancer immunotherapy, and strategies for effective and tolerable Treg-targeted therapy.
Keywords: Treg-targeted therapy; immune checkpoint inhibitors; immune suppression.
© The Japanese Society for Immunology. 2016. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures

References
-
- Khattri R. Cox T. Yasayko S. A. and Ramsdell F. 2003. An essential role for Scurfin in CD4+CD25+ T regulatory cells. Nat. Immunol. 4:337. - PubMed
-
- Hori S. Nomura T. and Sakaguchi S. 2003. Control of regulatory T cell development by the transcription factor Foxp3. Science 299:1057. - PubMed
-
- Fontenot J. D. Gavin M. A. and Rudensky A. Y. 2003. Foxp3 programs the development and function of CD4+CD25+ regulatory T cells. Nat. Immunol. 4:330. - PubMed
-
- Sakaguchi S., Sakaguchi N., Asano M., et al. 1995. Immunologic self-tolerance maintained by activated T cells expressing IL-2 receptor alpha-chains (CD25). Breakdown of a single mechanism of self-tolerance causes variouss autoimmune diseases. J. Immunol. 155:1151. - PubMed
-
- Bennett C. L., Christie J., Ramsdell F., et al. 2001. Thse immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, X-linked syndrome (IPEX) is caused by mutations of FOXP3. Nat. Genet. 27:20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

