Exercise training prevents ventricular tachycardia in CPVT1 due to reduced CaMKII-dependent arrhythmogenic Ca2+ release
- PMID: 27161030
- PMCID: PMC4957490
- DOI: 10.1093/cvr/cvw095
Exercise training prevents ventricular tachycardia in CPVT1 due to reduced CaMKII-dependent arrhythmogenic Ca2+ release
Abstract
Aims: Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia type 1 (CPVT1) is caused by mutations in the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) that lead to disrupted Ca(2+) handling in cardiomyocytes and ventricular tachycardia. The aim of this study was to test whether exercise training could reduce the propensity for arrhythmias in mice with the CPVT1-causative missense mutation Ryr2-R2474S by restoring normal Ca(2+) handling.
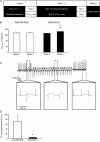
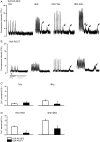
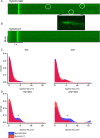
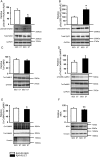
Methods and results: Ryr2-R2474S mice (RyR-RS) performed a 2 week interval treadmill exercise training protocol. Each exercise session comprised five 8 min intervals at 80-90% of the running speed at maximal oxygen uptake (VO2max) and 2 min active rest periods at 60%. VO2max increased by 10 ± 2% in exercise trained RyR-RS (ET), while no changes were found in sedentary controls (SED). RyR-RS ET showed fewer episodes of ventricular tachycardia compared with RyR-RS SED, coinciding with fewer Ca(2+) sparks and waves, less diastolic Ca(2+) leak from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and lower phosphorylation levels at RyR2 sites associated with Ca(2) (+)-calmodulin-dependent kinase type II (CaMKII) compared with RyR-RS SED. The CaMKII inhibitor autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide and also the antioxidant N-acetyl-l-cysteine reduced Ca(2+) wave frequency in RyR-RS equally to exercise training. Protein analysis as well as functional data indicated a mechanism depending on reduced levels of oxidized CaMKII after exercise training. Two weeks of detraining reversed the beneficial effects of the interval treadmill exercise training protocol in RyR-RS ET.
Conclusion: Long-term effects of interval treadmill exercise training reduce ventricular tachycardia episodes in mice with a CPVT1-causative Ryr2 mutation through lower CaMKII-dependent phosphorylation of RyR2.
Keywords: Arrhythmias; CPVT1; Ca2+ homeostasis; CaMKII; Exercise training.
Published on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology. All rights reserved. © The Author 2016. For permissions please email: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures



References
-
- Leenhardt A, Lucet V, Denjoy I, Grau F, Ngoc DD, Coumel P. Catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in children. A 7-year follow-up of 21 patients. Circulation 1995;91:1512–1519. - PubMed
-
- Lehnart SE, Wehrens XH, Laitinen PJ, Reiken SR, Deng SX, Cheng Z, Landry DW, Kontula K, Swan H, Marks AR. Sudden death in familial polymorphic ventricular tachycardia associated with calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor) leak. Circulation 2004;109:3208–3214. - PubMed
-
- Priori SG, Napolitano C, Memmi M, Colombi B, Drago F, Gasparini M, DeSimone L, Coltorti F, Bloise R, Keegan R, Cruz Filho FE, Vignati G, Benatar A, DeLogu A. Clinical and molecular characterization of patients with catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia. Circulation 2002;106:69–74. - PubMed
-
- Lahat H, Pras E, Eldar M. A missense mutation in CASQ2 is associated with autosomal recessive catecholamine-induced polymorphic ventricular tachycardia in Bedouin families from Israel. Ann Med 2004;36(Suppl. 1):87–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

