Evidence for the involvement of ASIC3 in sensory mechanotransduction in proprioceptors
- PMID: 27161260
- PMCID: PMC4866049
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11460
Evidence for the involvement of ASIC3 in sensory mechanotransduction in proprioceptors
Abstract
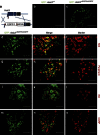
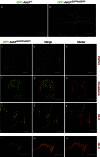
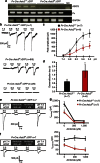
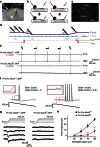
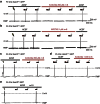
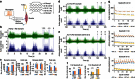
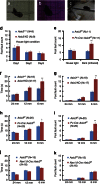
Acid-sensing ion channel 3 (ASIC3) is involved in acid nociception, but its possible role in neurosensory mechanotransduction is disputed. We report here the generation of Asic3-knockout/eGFPf-knockin mice and subsequent characterization of heterogeneous expression of ASIC3 in the dorsal root ganglion (DRG). ASIC3 is expressed in parvalbumin (Pv+) proprioceptor axons innervating muscle spindles. We further generate a floxed allele of Asic3 (Asic3(f/f)) and probe the role of ASIC3 in mechanotransduction in neurite-bearing Pv+ DRG neurons through localized elastic matrix movements and electrophysiology. Targeted knockout of Asic3 disrupts spindle afferent sensitivity to dynamic stimuli and impairs mechanotransduction in Pv+ DRG neurons because of substrate deformation-induced neurite stretching, but not to direct neurite indentation. In behavioural tasks, global knockout (Asic3(-/-)) and Pv-Cre::Asic3(f/f) mice produce similar deficits in grid and balance beam walking tasks. We conclude that, at least in mouse, ASIC3 is a molecular determinant contributing to dynamic mechanosensitivity in proprioceptors.
Figures
References
-
- Chalfie M. Neurosensory mechanotransduction. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 10, 44–52 (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

