Most neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies target novel epitopes requiring both Lassa virus glycoprotein subunits
- PMID: 27161536
- PMCID: PMC4866400
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11544
Most neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies target novel epitopes requiring both Lassa virus glycoprotein subunits
Abstract
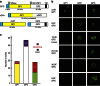
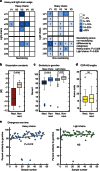
Lassa fever is a severe multisystem disease that often has haemorrhagic manifestations. The epitopes of the Lassa virus (LASV) surface glycoproteins recognized by naturally infected human hosts have not been identified or characterized. Here we have cloned 113 human monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) specific for LASV glycoproteins from memory B cells of Lassa fever survivors from West Africa. One-half bind the GP2 fusion subunit, one-fourth recognize the GP1 receptor-binding subunit and the remaining fourth are specific for the assembled glycoprotein complex, requiring both GP1 and GP2 subunits for recognition. Notably, of the 16 mAbs that neutralize LASV, 13 require the assembled glycoprotein complex for binding, while the remaining 3 require GP1 only. Compared with non-neutralizing mAbs, neutralizing mAbs have higher binding affinities and greater divergence from germline progenitors. Some mAbs potently neutralize all four LASV lineages. These insights from LASV human mAb characterization will guide strategies for immunotherapeutic development and vaccine design.
Conflict of interest statement
The Viral Hemorrhagic Fever Consortium (
Figures






References
-
- Monath T. P., Newhouse V. F., Kemp G. E., Setzer H. W. & Cacciapuoti A. Lassa virus isolation from Mastomys natalensis rodents during an epidemic in Sierra Leone. Science 185, 263–265 (1974). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- U01 AI082119/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI081982/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R13 AI104216/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007480/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI067927/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R44 AI115754/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- K12 HD043451/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U19 AI109762/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AI070530/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI121550/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI121840/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R44 AI088843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103501/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI104621/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UC1 AI067188/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R43 AI088843/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

