Lung stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastases: comparison of oligo-recurrence and sync-oligometastases
- PMID: 27162324
- PMCID: PMC4957009
- DOI: 10.1093/jjco/hyw047
Lung stereotactic radiotherapy for oligometastases: comparison of oligo-recurrence and sync-oligometastases
Abstract
Background: Oligometastases can be divided into sync-oligometastases and oligo-recurrence. The difference is whether the primary site is uncontrolled or controlled. The goal of this multicenter study was to evaluate treatment outcomes and factors affecting survival after stereotactic body radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases.
Methods: The information after stereotactic body radiotherapy from January 2004 to April 2014 was retrospectively collected. Ninety-six patients (65 males, 31 females) were enrolled. Ten cases (10%) were sync-oligometastases, 79 cases (82%) were oligo-recurrences and 7 (7%) were unclassified oligometastases with <6 months of disease-free interval. The median disease-free interval between initial therapy and stereotactic body radiotherapy was 24 months. The median calculated biological effective dose was 105.6 Gy.
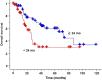
Results: The median follow-up period was 32 months for survivors. The 3-year overall survival and relapse-free survival rates were 53% and 32%, respectively. No Grade 5 toxicity occurred. The median overall survival was 23.9 months for sync-oligometastases and 66.6 months for oligo-recurrence (P = 0.0029). On multivariate analysis, sync-oligometastases and multiple oligometastatic tumors were significant unfavorable factors for both overall survival and relapse-free survival.
Conclusions: In stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastatic lung tumors, the state of oligo-recurrence has the potential of a significant prognostic factor for survival.
Keywords: SBRT; oligo-recurrence; pulmonary oligometastases; sync-oligometastases.
© The Author 2016. Published by Oxford University Press.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Oligo-recurrence predicts favorable prognosis of brain-only oligometastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer treated with stereotactic radiosurgery or stereotactic radiotherapy: a multi-institutional study of 61 subjects.BMC Cancer. 2016 Aug 19;16(1):659. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2680-8. BMC Cancer. 2016. PMID: 27542716 Free PMC article.
-
Stereotactic Body Radiotherapy Results for Pulmonary Oligometastases: A Two-Institution Collaborative Investigation.Anticancer Res. 2015 Sep;35(9):4903-8. Anticancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26254386 Clinical Trial.
-
Pulmonary Oligometastases Treated by Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy: A Nationwide Survey of 1,378 Patients.Anticancer Res. 2020 Jan;40(1):393-399. doi: 10.21873/anticanres.13965. Anticancer Res. 2020. PMID: 31892592
-
Stereotactic body radiotherapy for oligometastases.Lancet Oncol. 2013 Jan;14(1):e28-37. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(12)70510-7. Lancet Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23276369 Review.
-
Stereotactic ablative radiotherapy for pulmonary oligometastases and oligometastatic lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2014 Oct;9(10):1426-33. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0000000000000317. J Thorac Oncol. 2014. PMID: 25170641 Review.
Cited by
-
Stereotactic robotic body radiotherapy for patients with oligorecurrent pulmonary metastases.BMC Cancer. 2020 May 8;20(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-06906-1. BMC Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32384918 Free PMC article.
-
Oligometastases of Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 7;16(4):704. doi: 10.3390/cancers16040704. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38398095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligo-Recurrence in Lung Cancer; The Most Curable State Among Advanced Disease?Cancers (Basel). 2024 Dec 6;16(23):4086. doi: 10.3390/cancers16234086. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39682272 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oligometastases: history and future vision of breast cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2020 Aug;9(8):5028-5031. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-325. Transl Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 35117867 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Salvage radiotherapy for regional lymph node oligo-recurrence after radical surgery of non-small cell lung cancer.Thorac Cancer. 2017 Nov;8(6):620-629. doi: 10.1111/1759-7714.12497. Epub 2017 Sep 14. Thorac Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28906073 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

