Protective effect of black raspberry seed containing anthocyanins against oxidative damage to DNA, protein, and lipid
- PMID: 27162401
- PMCID: PMC4837709
- DOI: 10.1007/s13197-015-2094-7
Protective effect of black raspberry seed containing anthocyanins against oxidative damage to DNA, protein, and lipid
Abstract
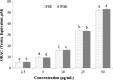
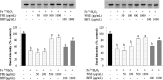
This study aimed to determine bioactive components and radical scavenging capacity of black raspberry seed extracts as byproducts obtaining during the juice (FSE) and wine (WSE) making process. Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside was identified as a major anthocyanin and the total anthocyanin contents of fresh and wine seed were 78.24 and 41.61 mg/100 g of dry weight, respectively. The total phenolic and flavonoid contents of FSE and WSE were 2.31 g gallic acid equivalent (GAE) and 360.95 mg catechin equivalent (CE), and 2.44 g GAE and 379.54 mg CE per 100 g dry weight, respectively. The oxygen radical absorbance capacity (ORAC) values were 1041.9 μM TE/g for FSE and 1060.4 μM TE/g for WSE. Pretreatment of the FSE and WSE inhibited the generation of intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS), DNA and protein damage induced by hydroxyl radicals, and Fe(3+)/ascorbic acid-induced lipid peroxidation in a dose dependent manner. WSE more effectively protected from oxidative damage than FSE. Results from the current study suggest that black raspberry seeds as byproducts from juice and wine processing could be potential sources for natural antioxidants.
Keywords: Antioxidants; Black raspberry seeds; Byproducts; Juice and winemaking; Rubus coreanus Miq.; Seed extract.
Figures




References
-
- Arts IC, Hollman PC. Polyphenols and disease risk in epidemiologic studies. Am J Clin Nutr. 2005;81:317–325. - PubMed
-
- Bahramikia S, Ardestani A, Yazdanparast R. Protective effects of four Iranian medicinal plants against free radical mediated protein oxidation. Food Chem. 2009;115:37–42. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.11.054. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
