A Comparison of Rebound to Indentation Tonometry in Supine Sedated Children with Glaucoma
- PMID: 27162450
- PMCID: PMC4845616
- DOI: 10.4103/0974-9233.179707
A Comparison of Rebound to Indentation Tonometry in Supine Sedated Children with Glaucoma
Abstract
Purpose: To compare intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements by rebound tonometry (Icare PRO; Icare Finland Oy, Helsinki, Finland) to measurements by indentation tonometry (Pneumotonometer Model 30 classic and Tono-Pen XL; Reichert, Buffalo, NY, USA) in supine sedated children with glaucoma.
Methods: Prospective comparative observational study of Saudi Arabian children with glaucoma undergoing chloral hydrate sedation for ophthalmic examination (February 2012 - February 2013). Nonglaucomatous eyes were included as controls. Eyes with corneal scars or prior corneal transplant or lamellar surgery were excluded.
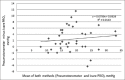
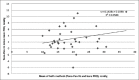
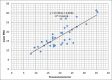
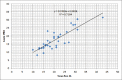
Results: Fifty-two eyes (26 OD, 26 OS) of 28 children were included. Thirty-six eyes had glaucoma (32 primary congenital glaucoma, two Sturge-Weber related, and two aphakia related). Sixteen eyes did not have glaucoma (six with pediatric cataract, five normal eyes, two strabismic eyes, two eyes with simple megalocornea, and one eye had peripheral corneal laceration repair. In the glaucoma group, the mean IOP was 17.55 ± 5.97 mmHg (range, 8-31.5 mmHg) with the Icare PRO and 20 ± 6.4 mmHg (range, 8-35.5 mmHg) with the Pneumotonometer from 20.47 ± 6.81 mmHg (range, 10-43 mmHg) with the Tono-Pen XL. The Icare PRO readings were significantly lower than each of the indentation tonometers. For the control group, there was no statistically significant difference in IOP measured by the Icare PRO and the indentation tonometers.
Conclusions: In this population of supine sedated children with glaucoma, IOP measurements with the Icare PRO tend to be lower than readings from the Pneumotonometer and Tono-Pen XL.
Keywords: Chloral hydrate; Indentation tonometry; Pediatric glaucoma; Rebound tonometry.
Figures
References
-
- Kontiola A. A new electromechanical method for measuring intraocular pressure. Doc Ophthalmol. 1996;93:265–76. - PubMed
-
- Sahin A, Basmak H, Niyaz L, Yildirim N. Reproducibility and tolerability of the ICare rebound tonometer in school children. J Glaucoma. 2007;16:185–8. - PubMed
-
- Flemmons MS, Hsiao YC, Dzau J, Asrani S, Jones S, Freedman SF. Icare rebound tonometry in children with known and suspected glaucoma. J AAPOS. 2011;15:153–7. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi NG, Prakalapakorn SG, El-Dairi MA, Jones SK, Freedman SF. Icare ONE rebound versus Goldmann applanation tonometry in children with known or suspected glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol. 2012;154:843–9.e1. - PubMed
-
- Grigorian F, Grigorian AP, Olitsky SE. The use of the iCare tonometer reduced the need for anesthesia to measure intraocular pressure in children. J AAPOS. 2012;16:508–10. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

