Metabologenomics: Correlation of Microbial Gene Clusters with Metabolites Drives Discovery of a Nonribosomal Peptide with an Unusual Amino Acid Monomer
- PMID: 27163034
- PMCID: PMC4827660
- DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.5b00331
Metabologenomics: Correlation of Microbial Gene Clusters with Metabolites Drives Discovery of a Nonribosomal Peptide with an Unusual Amino Acid Monomer
Abstract
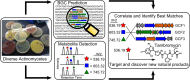
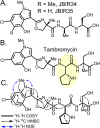
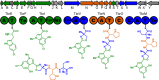
For more than half a century the pharmaceutical industry has sifted through natural products produced by microbes, uncovering new scaffolds and fashioning them into a broad range of vital drugs. We sought a strategy to reinvigorate the discovery of natural products with distinctive structures using bacterial genome sequencing combined with metabolomics. By correlating genetic content from 178 actinomycete genomes with mass spectrometry-enabled analyses of their exported metabolomes, we paired new secondary metabolites with their biosynthetic gene clusters. We report the use of this new approach to isolate and characterize tambromycin, a new chlorinated natural product, composed of several nonstandard amino acid monomeric units, including a unique pyrrolidine-containing amino acid we name tambroline. Tambromycin shows antiproliferative activity against cancerous human B- and T-cell lines. The discovery of tambromycin via large-scale correlation of gene clusters with metabolites (a.k.a. metabologenomics) illuminates a path for structure-based discovery of natural products at a sharply increased rate.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of the Tyrobetaine Natural Products and Their Biosynthetic Gene Cluster via Metabologenomics.ACS Chem Biol. 2018 Apr 20;13(4):1029-1037. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.7b01089. Epub 2018 Mar 13. ACS Chem Biol. 2018. PMID: 29510029 Free PMC article.
-
Natural product discovery: past, present, and future.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Mar;43(2-3):155-76. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1723-5. Epub 2016 Jan 6. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26739136 Review.
-
Total Synthesis of Tambromycin by Combining Chemocatalytic and Biocatalytic C-H Functionalization.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018 Apr 23;57(18):5037-5041. doi: 10.1002/anie.201801165. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2018. PMID: 29481729
-
A metabologenomics strategy for rapid discovery of polyketides derived from modular polyketide synthases.Chem Sci. 2024 Nov 4;16(4):1696-1706. doi: 10.1039/d4sc04174g. eCollection 2025 Jan 22. Chem Sci. 2024. PMID: 39568943 Free PMC article.
-
In depth natural product discovery - Myxobacterial strains that provided multiple secondary metabolites.Biotechnol Adv. 2020 Mar-Apr;39:107480. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107480. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Biotechnol Adv. 2020. PMID: 31707075 Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomics and Metabolomics Analysis Reveal the Regulation Mechanism of Linoleate Isomerase Activity and Function in Propionibacterium acnes.ACS Omega. 2023 Dec 18;9(1):1643-1655. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c08243. eCollection 2024 Jan 9. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 38222669 Free PMC article.
-
Ranking microbial metabolomic and genomic links in the NPLinker framework using complementary scoring functions.PLoS Comput Biol. 2021 May 4;17(5):e1008920. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008920. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2021. PMID: 33945539 Free PMC article.
-
Discovery of the Biosynthetic Machinery for Stravidins, Biotin Antimetabolites.ACS Chem Biol. 2020 May 15;15(5):1134-1140. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00890. Epub 2020 Jan 9. ACS Chem Biol. 2020. PMID: 31887014 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics and Genomics Enable the Discovery of a New Class of Nonribosomal Peptidic Metallophores from a Marine Micromonospora.J Am Chem Soc. 2023 Jan 11;145(1):58-69. doi: 10.1021/jacs.2c06410. Epub 2022 Dec 19. J Am Chem Soc. 2023. PMID: 36535031 Free PMC article.
-
Genome Analysis of Streptomyces nojiriensis JCM 3382 and Distribution of Gene Clusters for Three Antibiotics and an Azasugar across the Genus Streptomyces.Microorganisms. 2021 Aug 25;9(9):1802. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms9091802. Microorganisms. 2021. PMID: 34576698 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cragg G. M.; Newman D. J. Natural products: a continuing source of novel drug leads. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Gen. Subj. 2013, 1830 (6), 3670–3695. 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.008. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Newman D. J.; Cragg G. M. Natural products as sources of new drugs over the last 25 years. J. Nat. Prod. 2007, 70 (3), 461–477. 10.1021/np068054v. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bentley S. D.; Chater K. F.; Cerdeno-Tarraga A. M.; Challis G. L.; Thomson N. R.; James K. D.; Harris D. E.; Quail M. A.; Kieser H.; Harper D.; Bateman A.; Brown S.; Chandra G.; Chen C. W.; Collins M.; Cronin A.; Fraser A.; Goble A.; Hidalgo J.; Hornsby T.; Howarth S.; Huang C. H.; Kieser T.; Larke L.; Murphy L.; Oliver K.; O’Neil S.; Rabbinowitsch E.; Rajandream M. A.; Rutherford K.; Rutter S.; Seeger K.; Saunders D.; Sharp S.; Squares R.; Squares S.; Taylor K.; Warren T.; Wietzorrek A.; Woodward J.; Barrell B. G.; Parkhill J.; Hopwood D. A. Complete genome sequence of the model actinomycete Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). Nature 2002, 417 (6885), 141–147. 10.1038/417141a. - DOI - PubMed
- Oliynyk M.; Samborskyy M.; Lester J. B.; Mironenko T.; Scott N.; Dickens S.; Haydock S. F.; Leadlay P. F. Complete genome sequence of the erythromycin-producing bacterium Saccharopolyspora erythraea NRRL23338. Nat. Biotechnol. 2007, 25 (4), 447–453. 10.1038/nbt1297. - DOI - PubMed
- Udwary D. W.; Zeigler L.; Asolkar R. N.; Singan V.; Lapidus A.; Fenical W.; Jensen P. R.; Moore B. S. Genome sequencing reveals complex secondary metabolome in the marine actinomycete Salinispora tropica. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2007, 104 (25), 10376–10381. 10.1073/pnas.0700962104. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

