Conformational Plasticity of the NNRTI-Binding Pocket in HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase: A Fluorine Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study
- PMID: 27163463
- PMCID: PMC4955860
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00113
Conformational Plasticity of the NNRTI-Binding Pocket in HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase: A Fluorine Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Study
Abstract
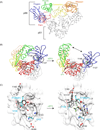
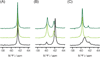
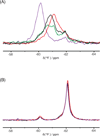
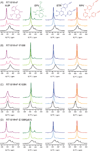
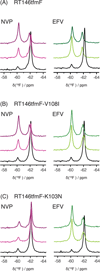
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase (RT) is a major drug target in the treatment of HIV-1 infection. RT inhibitors currently in use include non-nucleoside, allosteric RT inhibitors (NNRTIs), which bind to a hydrophobic pocket, distinct from the enzyme's active site. We investigated RT-NNRTI interactions by solution (19)F nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR), using singly (19)F-labeled RT proteins. Comparison of (19)F chemical shifts of fluorinated RT and drug-resistant variants revealed that the fluorine resonance is a sensitive probe for identifying mutation-induced changes in the enzyme. Our data show that in the unliganded enzyme, the NNRTI-binding pocket is highly plastic and not locked into a single conformation. Upon inhibitor binding, the binding pocket becomes rigidified. In the inhibitor-bound state, the (19)F signal of RT is similar to that of drug-resistant mutant enzymes, distinct from what is observed for the free state. Our results demonstrate the power of (19)F NMR spectroscopy to characterize conformational properties using selectively (19)F-labeled protein.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Lys103Asn mutation of HIV-1 RT: a novel mechanism of drug resistance.J Mol Biol. 2001 Jun 1;309(2):437-45. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.2001.4648. J Mol Biol. 2001. PMID: 11371163
-
Crystal structures of clinically relevant Lys103Asn/Tyr181Cys double mutant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase in complexes with ATP and non-nucleoside inhibitor HBY 097.J Mol Biol. 2007 Jan 5;365(1):77-89. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2006.08.097. Epub 2006 Sep 15. J Mol Biol. 2007. PMID: 17056061
-
Effect of a bound non-nucleoside RT inhibitor on the dynamics of wild-type and mutant HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.J Am Chem Soc. 2005 Dec 14;127(49):17253-60. doi: 10.1021/ja053973d. J Am Chem Soc. 2005. PMID: 16332074
-
HIV-1 reverse transcriptase connection subdomain mutations involved in resistance to approved non-nucleoside inhibitors.Antiviral Res. 2011 Nov;92(2):139-49. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2011.08.020. Epub 2011 Aug 28. Antiviral Res. 2011. PMID: 21896288 Review.
-
Conformational changes in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase induced by nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor binding.Curr HIV Res. 2004 Oct;2(4):323-32. doi: 10.2174/1570162043351093. Curr HIV Res. 2004. PMID: 15544453 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Conformational Changes in HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase that Facilitate Its Maturation.Structure. 2019 Oct 1;27(10):1581-1593.e3. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2019.08.004. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Structure. 2019. PMID: 31471129 Free PMC article.
-
Meet the IUPAB councilor - Angela M. Gronenborn.Biophys Rev. 2021 Nov 19;13(6):835-838. doi: 10.1007/s12551-021-00886-7. eCollection 2021 Dec. Biophys Rev. 2021. PMID: 35059003 Free PMC article.
-
Small Conformational Changes Underlie Evolution of Resistance to NNRTI in HIV Reverse Transcriptase.Biophys J. 2020 May 19;118(10):2489-2501. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2020.04.008. Epub 2020 Apr 16. Biophys J. 2020. PMID: 32348721 Free PMC article.
-
Relative domain orientation of the L289K HIV-1 reverse transcriptase monomer.Protein Sci. 2022 May;31(5):e4307. doi: 10.1002/pro.4307. Protein Sci. 2022. PMID: 35481647 Free PMC article.
-
Large Multidomain Protein NMR: HIV-1 Reverse Transcriptase Precursor in Solution.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 15;21(24):9545. doi: 10.3390/ijms21249545. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33333923 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Looney D, Ma A, Johns S. HIV therapy-the state of art. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015;389:1–29. - PubMed
-
- Kohlstaedt LA, Wang J, Friedman JM, Rice PA. Crystal structure at 3.5 A resolution of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase complexed with an inhibitor. …. 1992;256:1783–1790. - PubMed
-
- Hsiou Y, Ding J, Das K, Clark AD, Jr, Hughes SH, Arnold EE. Structure of unliganded HIV-1 reverse transcriptase at 2.7 å resolution: implications of conformational changes for polymerization and inhibition mechanisms. Structure. 1996;4:853–860. - PubMed
-
- Lansdon EB, Brendza KM, Hung M, Wang R, Mukund S, Jin D, Birkus G, Kutty N, Liu X. Crystal structures of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase with etravirine (TMC125) and rilpivirine (TMC278): implications for drug design. J. Med. Chem. 2010;53:4295–4299. - PubMed
-
- Milton J, Weaver KL, Short SA. Structural basis for the resilience of efavirenz (DMP-266) to drug resistance mutations in HIV-1 reverse transcriptase. Structure. 2000;8:1089–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

