Molecular and cellular aspects of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 27163751
- PMCID: PMC5099115
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbr.2016.05.008
Molecular and cellular aspects of age-related cognitive decline and Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
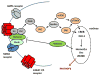
As the population of people aged 60 or older continues to rise, it has become increasingly important to understand the molecular basis underlying age-related cognitive decline. In fact, a better understanding of aging biology will help us identify ways to maintain high levels of cognitive functioning throughout the aging process. Many cellular and molecular aspects of brain aging are shared with other organ systems; however, certain age-related changes are unique to the nervous system due to its structural, cellular and molecular complexity. Importantly, the brain appears to show differential changes throughout the aging process, with certain regions (e.g. frontal and temporal regions) being more vulnerable than others (e.g. brain stem). Within the medial temporal lobe, the hippocampus is especially susceptible to age-related changes. The important role of the hippocampus in age-related cognitive decline and in vulnerability to disease processes such as Alzheimer's disease has prompted this review, which will focus on the complexity of changes that characterize aging, and on the molecular connections that exist between normal aging and Alzheimer's disease. Finally, it will discuss behavioral interventions and emerging insights for promoting healthy cognitive aging.
Keywords: Aging; Alzheimer’s disease; Cognition; Hippocampus; Molecular mechanisms.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Aging Statistics, Administration for Community Living Administration on Aging. 2014 http://www.aoa.gov/Aging_Statistics/
-
- Knierim JJ. The hippocampus. Curr Biol. 2015;25:R1116–R1121. - PubMed
-
- Colgin LL, Moser EI, Moser MB. Understanding memory through hippocampal remapping. Trends Neurosci. 2008;31:469–477. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

