Mouse Modeling of Obese Lung Disease. Insights and Caveats
- PMID: 27163945
- PMCID: PMC4979373
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0063PS
Mouse Modeling of Obese Lung Disease. Insights and Caveats
Abstract
As the obesity epidemic has worsened, its impact on lung health and disease has become progressively evident. The interactions between obesity and the accompanying metabolic syndrome and diseases such as asthma, pneumonia, and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) have proven complex and often counterintuitive in human studies. Hence, there is a growing need for relevant experimental approaches to understand the interactions between obesity and the lung. To this end, researchers have increasingly exploited mouse models combining both obesity and lung diseases, including ARDS, pneumonia, and asthma. Such models have both complemented and advanced the understanding we have gained from clinical studies and have allowed elegant dissections of obesity's effects on the pathogenesis of lung disease. Yet these models come with several critically important caveats that we must reflect on when interpreting their results.
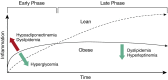
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Comparative Study of Lung Host Defense in Murine Obesity Models. Insights into Neutrophil Function.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 Aug;55(2):188-200. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0042OC. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 27128821 Free PMC article.
-
Autophagy and Obesity-Related Lung Disease.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016 May;54(5):636-46. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0045PS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2016. PMID: 26900794 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mouse Models of Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome: A Review of Analytical Approaches, Pathologic Features, and Common Measurements.Toxicol Pathol. 2015 Dec;43(8):1074-92. doi: 10.1177/0192623315598399. Epub 2015 Aug 21. Toxicol Pathol. 2015. PMID: 26296628 Review.
-
Acute respiratory distress syndrome caused by pulmonary and extrapulmonary injury: a comparative CT study.Radiology. 2001 Mar;218(3):689-93. doi: 10.1148/radiology.218.3.r01mr31689. Radiology. 2001. PMID: 11230641
-
Immunological characteristics and management considerations in obese patients with asthma.Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015;11(7):793-803. doi: 10.1586/1744666X.2015.1040394. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Expert Rev Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25914932 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Integrative Physiology of Pneumonia.Physiol Rev. 2018 Jul 1;98(3):1417-1464. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00032.2017. Physiol Rev. 2018. PMID: 29767563 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chair's Summary: Obesity and Associated Changes in Metabolism, Implications for Lung Diseases.Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017 Nov;14(Suppl_5):S314-S315. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201702-116AW. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2017. PMID: 29161083 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Aberrant pulmonary immune response of obese mice to periodontal infection.Open Life Sci. 2022 Aug 17;17(1):991-1000. doi: 10.1515/biol-2022-0089. eCollection 2022. Open Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36060644 Free PMC article.
-
IL-33, diet-induced obesity, and pulmonary responses to ozone.Respir Res. 2020 Apr 23;21(1):98. doi: 10.1186/s12931-020-01361-9. Respir Res. 2020. PMID: 32326950 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Obesity in the Immunopathogenesis of COVID-19 Respiratory Disease and Critical Illness.Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021 Jul;65(1):13-21. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2020-0236TR. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 33797351 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adams KF, Schatzkin A, Harris TB, Kipnis V, Mouw T, Ballard-Barbash R, Hollenbeck A, Leitzmann MF. Overweight, obesity, and mortality in a large prospective cohort of persons 50 to 71 years old. N Engl J Med. 2006;355:763–778. - PubMed
-
- Flegal KM, Carroll MD, Ogden CL, Curtin LR. Prevalence and trends in obesity among US adults, 1999-2008. JAMA. 2010;303:235–241. - PubMed
-
- Rosenthal N, Brown S. The mouse ascending: perspectives for human-disease models. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9:993–999. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

