MRI sequences for the detection of individual lymph nodes in regional breast radiotherapy planning
- PMID: 27164032
- PMCID: PMC5257320
- DOI: 10.1259/bjr.20160072
MRI sequences for the detection of individual lymph nodes in regional breast radiotherapy planning
Abstract
Objective: In regional radiotherapy (RT) for patients with breast cancer, lymph node (LN) targets are delineated on CT, defined by anatomical boundaries. By identifying individual LNs, MRI-based delineations may reduce target volumes and thereby toxicity. We optimized MRI sequences for this purpose. Our aim was to evaluate the techniques for LN delineation in RT planning.
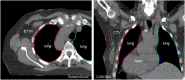
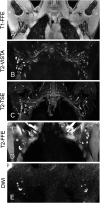
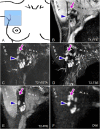
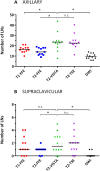
Methods: Supine MRI was explored at 1.5 T in RT position (arms in abduction). 5 MRI techniques were optimized in 10 and evaluated in 12 healthy female volunteers. The scans included one T1 weighted (T1w), three T2 weighted (T2w) and a diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI) technique. Quantitative evaluation was performed by scoring LN numbers per volunteer and per scan. Qualitatively, scans were assessed on seven aspects, including LN contrast, anatomical information and insensitivity to motion during acquisition.
Results: Two T2w fast spin-echo (FSE) methods showed the highest LN numbers (median 24 axillary), high contrast, excellent fat suppression and relative insensitivity to motion during acquisition. A third T2w sequence and DWI showed significantly fewer LNs (14 and 10) and proved unsuitable due to motion sensitivity and geometrical uncertainties. T1w MRI showed an intermediate number of LNs (17), provided valuable anatomical information, but lacked LN contrast.
Conclusion: Explicit LN imaging was achieved, in supine RT position, using MRI. Two T2w FSE techniques had the highest detection rates and were motion insensitive. T1w MRI showed anatomical information. MRI enables direct delineation of individual LNs.
Advances in knowledge: Our optimized MRI scans enable accurate target definition in MRI-guided regional breast RT and development of personalized treatments.
Figures

References
-
- Kakuda JT, Stuntz M, Trivedi V, Klein SR, Vargas HI. Objective assessment of axillary morbidity in breast cancer treatment. Am Surg 1999; 65: 995–8. - PubMed
-
- Giuliano AE, McCall L, Beitsch P, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz P, Leitch AM, et al. . Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 randomized trial. Ann Surg 2010; 252: 426–32; discussion 432–3. doi: 10.1097/SLA.0b013e3181f08f32 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

