Coupling Peptide Antigens to Virus-Like Particles or to Protein Carriers Influences the Th1/Th2 Polarity of the Resulting Immune Response
- PMID: 27164150
- PMCID: PMC4931632
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines4020015
Coupling Peptide Antigens to Virus-Like Particles or to Protein Carriers Influences the Th1/Th2 Polarity of the Resulting Immune Response
Abstract
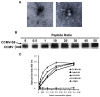
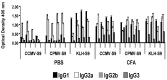
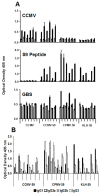
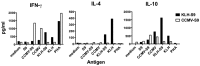
We have conjugated the S9 peptide, a mimic of the group B streptococcal type III capsular polysaccharide, to different carriers in an effort to elicit an optimal immune response. As carriers, we utilized the soluble protein keyhole limpet hemocyanin and virus-like particles (VLPs) from two plant viruses, Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus and Cowpea Mosaic Virus. We have found that coupling the peptide to the soluble protein elicits a Th2 immune response, as evidenced by the production of the peptide-specific IgG1 antibody and IL-4/IL-10 production in response to antigen stimulation, whereas the peptide conjugated to VLPs elicited a Th1 response (IgG2a, IFN-γ). Because the VLPs used as carriers package RNA during the assembly process, we hypothesize that this effect may result from the presence of nucleic acid in the immunogen, which affects the Th1/Th2 polarity of the response.
Keywords: Streptococcus agalactiae; antigen; capsular polysaccharide; group B streptococcus; mimotope; synthetic peptide.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-12 profoundly up-regulates the synthesis of antigen-specific complement-fixing IgG2a, IgG2b and IgG3 antibody subclasses in vivo.Eur J Immunol. 1995 Mar;25(3):823-9. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250329. Eur J Immunol. 1995. PMID: 7705414
-
The hepatitis B virus core and e antigens elicit different Th cell subsets: antigen structure can affect Th cell phenotype.J Virol. 1997 Mar;71(3):2192-201. doi: 10.1128/JVI.71.3.2192-2201.1997. J Virol. 1997. PMID: 9032353 Free PMC article.
-
IL-12, as an adjuvant, promotes a T helper 1 cell, but does not suppress a T helper 2 cell recall response.J Immunol. 1996 Feb 1;156(3):887-94. J Immunol. 1996. PMID: 8558014
-
Regulation of T-cell activation: differences among T-cell subsets.Immunol Rev. 1989 Oct;111:79-110. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1989.tb00543.x. Immunol Rev. 1989. PMID: 2534116 Review.
-
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) evades the human adaptive immune system by skewing the Th1/Th2 cytokine balance toward increased levels of Th2 cytokines and IgE, markers of allergy--a review.Virus Genes. 2006 Oct;33(2):235-52. doi: 10.1007/s11262-006-0064-x. Virus Genes. 2006. PMID: 16972040 Review.
Cited by
-
Hepatitis B core-based virus-like particles: A platform for vaccine development in plants.Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021 Feb 28;29:e00605. doi: 10.1016/j.btre.2021.e00605. eCollection 2021 Mar. Biotechnol Rep (Amst). 2021. PMID: 33732633 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Virus-like Particle Vaccines and Platforms for Vaccine Development.Viruses. 2023 May 2;15(5):1109. doi: 10.3390/v15051109. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37243195 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficient Purification of Cowpea Chlorotic Mottle Virus by a Novel Peptide Aptamer.Viruses. 2023 Mar 7;15(3):697. doi: 10.3390/v15030697. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 36992405 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in protein nanoparticle vaccine platforms to combat infectious disease.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2021 May;13(3):e1681. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1681. Epub 2020 Nov 8. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2021. PMID: 33164326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical and biological conjugation strategies for the development of multivalent protein vaccine nanoparticles.Biopolymers. 2023 Aug;114(8):e23563. doi: 10.1002/bip.23563. Epub 2023 Jul 25. Biopolymers. 2023. PMID: 37490564 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pincus S.H., Smith M.J., Burritt J.B., Glee P.M. Peptides that mimic the protective antigen of group B streptococcal type III capsular polysaccharide. J. Immunol. 1998;160:293–298. - PubMed
-
- Brumfield S., Willits D., Tang L., Johnson J.E., Douglas T., Young M. Heterologous expression of the modified coat protein of cowpea chlorotic mottle bromovirus results in the assembly of protein cages with altered architectures and function. J. Gen. Virol. 2004;85:1049–1053. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.19688-0. - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

