Myo-inositol changes precede amyloid pathology and relate to APOE genotype in Alzheimer disease
- PMID: 27164711
- PMCID: PMC4862247
- DOI: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002672
Myo-inositol changes precede amyloid pathology and relate to APOE genotype in Alzheimer disease
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to test whether in vivo levels of magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) metabolites myo-inositol (mI), N-acetylaspartate (NAA), and choline are abnormal already during preclinical Alzheimer disease (AD), relating these changes to amyloid or tau pathology, and functional connectivity.
Methods: In this cross-sectional multicenter study (a subset of the prospective Swedish BioFINDER study), we included 4 groups, representing the different stages of predementia AD: (1) cognitively healthy elderly with normal CSF β-amyloid 42 (Aβ42), (2) cognitively healthy elderly with abnormal CSF Aβ42, (3) patients with subjective cognitive decline and abnormal CSF Aβ42, (4) patients with mild cognitive decline and abnormal CSF Aβ42 (Ntotal = 352). Spectroscopic markers measured in the posterior cingulate/precuneus were considered alongside known disease biomarkers: CSF Aβ42, phosphorylated tau, total tau, [(18)F]-flutemetamol PET, f-MRI, and the genetic risk factor APOE.
Results: Amyloid-positive cognitively healthy participants showed a significant increase in mI/creatine and mI/NAA levels compared to amyloid-negative healthy elderly (p < 0.05). In amyloid-positive healthy elderly, mI/creatine and mI/NAA correlated with cortical retention of [(18)F] flutemetamol tracer ([Formula: see text] = 0.44, p = 0.02 and [Formula: see text] = 0.51, p = 0.01, respectively). Healthy elderly APOE ε4 carriers with normal CSF Aβ42 levels had significantly higher mI/creatine levels (p < 0.001) than ε4 noncarriers. Finally, elevated mI/creatine was associated with decreased functional connectivity within the default mode network (rpearson = -0.16, p = 0.02), independently of amyloid pathology.
Conclusions: mI levels are elevated already at asymptomatic stages of AD. Moreover, mI/creatine concentrations were increased in healthy APOE ε4 carriers with normal CSF Aβ42 levels, suggesting that mI levels may reveal regional brain consequences of APOE ε4 before detectable amyloid pathology.
© 2016 American Academy of Neurology.
Figures
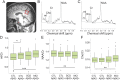
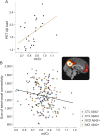
 = 0.42, t = 2.62, p = 0.02). (B) Association between mI/Cr in PCC/precuneus and functional connectivity. The sum of each participant's seed-voxel correlation within a normal connectivity mask correlated significantly with mI/Cr levels in the seed region across participants from all groups, rpearson = −0.16 (p = 0.02). The inset shows the seed position in precuneus (in blue) and the thresholded average normal connectivity of CSF Aβ42-negative controls used to define the normal connectivity mask. CTL Aβ42− = controls with CSF Aβ42 >530 ng/L; CTL Aβ42+ = controls with CSF Aβ42 ≤530 ng/L; SCD Aβ42+ = patients with subjective cognitive decline with CSF Aβ42 ≤530 ng/L; MCI Aβ42+ = patients with mild cognitive impairment with CSF Aβ42 ≤530 ng/L.
= 0.42, t = 2.62, p = 0.02). (B) Association between mI/Cr in PCC/precuneus and functional connectivity. The sum of each participant's seed-voxel correlation within a normal connectivity mask correlated significantly with mI/Cr levels in the seed region across participants from all groups, rpearson = −0.16 (p = 0.02). The inset shows the seed position in precuneus (in blue) and the thresholded average normal connectivity of CSF Aβ42-negative controls used to define the normal connectivity mask. CTL Aβ42− = controls with CSF Aβ42 >530 ng/L; CTL Aβ42+ = controls with CSF Aβ42 ≤530 ng/L; SCD Aβ42+ = patients with subjective cognitive decline with CSF Aβ42 ≤530 ng/L; MCI Aβ42+ = patients with mild cognitive impairment with CSF Aβ42 ≤530 ng/L.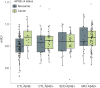
Comment in
-
MR spectroscopy, APOE genotype, and evolving β-amyloid pathology: What is being detected and when.Neurology. 2016 May 10;86(19):1750-1. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002680. Epub 2016 Apr 15. Neurology. 2016. PMID: 27164709 No abstract available.
References
-
- Jessen F, Block W, Traber F, et al. Proton MR spectroscopy detects a relative decrease of N-acetylaspartate in the medial temporal lobe of patients with AD. Neurology 2000;55:684–688. - PubMed
-
- Huang W, Alexander GE, Chang L, et al. Brain metabolite concentration and dementia severity in Alzheimer's disease: a (1)H MRS study. Neurology 2001;57:626–632. - PubMed
-
- Corder E, Saunders A, Strittmatter W, et al. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer's disease in late onset families. Science 1993;261:921–923. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
