Transient receptor potential canonical 5 (TRPC5) protects against pain and vascular inflammation in arthritis and joint inflammation
- PMID: 27165180
- PMCID: PMC5264234
- DOI: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208886
Transient receptor potential canonical 5 (TRPC5) protects against pain and vascular inflammation in arthritis and joint inflammation
Abstract
Objective: Transient receptor potential canonical 5 (TRPC5) is functionally expressed on a range of cells including fibroblast-like synoviocytes, which play an important role in arthritis. A role for TRPC5 in inflammation has not been previously shown in vivo. We investigated the contribution of TRPC5 in arthritis.
Methods: Male wild-type and TRPC5 knockout (KO) mice were used in a complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA)-induced unilateral arthritis model, assessed over 14 days. Arthritis was determined by measurement of knee joint diameter, hindlimb weightbearing asymmetry and pain behaviour. Separate studies involved chronic pharmacological antagonism of TRPC5 channels. Synovium from human postmortem control and inflammatory arthritis samples were investigated for TRPC5 gene expression.
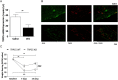
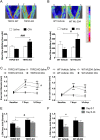
Results: At baseline, no differences were observed. CFA-induced arthritis resulted in increased synovitis in TRPC5 KO mice assessed by histology. Additionally, TRPC5 KO mice demonstrated reduced ispilateral weightbearing and nociceptive thresholds (thermal and mechanical) following CFA-induced arthritis. This was associated with increased mRNA expression of inflammatory mediators in the ipsilateral synovium and increased concentration of cytokines in synovial lavage fluid. Chronic treatment with ML204, a TRPC5 antagonist, augmented weightbearing asymmetry, secondary hyperalgesia and cytokine concentrations in the synovial lavage fluid. Synovia from human inflammatory arthritis demonstrated a reduction in TRPC5 mRNA expression.
Conclusions: Genetic deletion or pharmacological blockade of TRPC5 results in an enhancement in joint inflammation and hyperalgesia. Our results suggest that activation of TRPC5 may be associated with an endogenous anti-inflammatory/analgesic pathway in inflammatory joint conditions.
Keywords: Arthritis; Inflammation; Synovitis.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
Figures




References
-
- Walsh DA, McWilliams DF. Mechanisms, impact and management of pain in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 2014;10:581–92. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2014.64 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, et al. . 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1580–8. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.138461 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Clapham DE. TRP channels as cellular sensors. Nature 2003;426:517–24. doi:10.1038/nature02196 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fernandes ES, Russell FA, Spina D, et al. . A distinct role for transient receptor potential ankyrin 1, in addition to transient receptor potential vanilloid 1, in tumor necrosis factor α-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia and Freund's complete adjuvant-induced monarthritis. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:819–29. doi:10.1002/art.30150 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Aubdool AA, Graepel R, Kodji X, et al. . TRPA1 is essential for the vascular response to environmental cold exposure. Nat Commun 2014;5:5732 doi:10.1038/ncomms6732 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

