[Levels of surfactant proteins A and D in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of children with pneumonia and their relationships with clinical characteristics]
- PMID: 27165584
- PMCID: PMC7390360
- DOI: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2016.05.002
[Levels of surfactant proteins A and D in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid of children with pneumonia and their relationships with clinical characteristics]
Abstract
Objective: To observe the levels of pulmonary surfactant proteins A and D (SP-A, SP-D) in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of children with pneumonia, and to explore their relationships with clinical characteristics.
Methods: Thirty-five children with pneumonia were enrolled in this study. Differential cell counts were obtained by Countstar counting board. The levels of SP-A and SP-D in BALF were detected using ELISA.
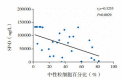
Results: In children with pneumonia, SP-D levels were significantly higher than SP-A levels (P<0.001). SP-D levels were negatively correlated with the neutrophil percentage in BALF (r(s)=-0.5255, P<0.01). SP-D levels in BALF in children with increased blood C-reactive protein levels (>8 mg/L) were significantly lower than in those with a normal level of C-reactive protein (P<0.05). Compared with those in children without wheezing, SP-D levels in children with wheezing were significantly lower (P<0.01). There was no correlation between SP-A levels and clinical characteristics.
Conclusions: SP-D levels in BALF are significantly higher than SP-A levels, and have a certain correlation with clinical characteristics in children with pneumonia. As a protective factor, SP-D plays a more important role than SP-A in regulating the immune and inflammatory responses.
目的: 观察肺表面活性蛋白A、D(SP-A、SP-D)在肺炎患儿支气管肺泡灌洗液(BALF)中的表达, 探讨SP-A、SP-D与肺炎患儿临床特征的相关性。
方法: 35例肺炎患儿纳入研究, 对其肺泡灌洗液细胞进行分类计数, 采用酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)检测患儿BALF中SP-A和SP-D水平。
结果: 患儿BALF中SP-D水平显著高于SP-A水平(P < 0.001)。BALF中SP-D水平与中性粒细胞百分比成负相关(rs=-0.5255, P < 0.01);血C反应蛋白水平升高(>8mg/L)的患儿BALF中SP-D水平明显低于C反应蛋白正常的患儿(P < 0.05);有喘息症状的患儿BALF中SP-D水平明显低于无喘息症状者(P < 0.01)。BALF中的SP-A与临床特征无明显关系(P>0.05)。
结论: 肺炎患儿BALF中SP-D的表达显著高于SP-A, 与肺炎患儿的临床特征有一定相关性, 作为一种保护性因子在调节免疫及炎症反应中发挥着比SP-A更重要的作用。
References
-
- 刘 继贤, 盛 锦云, 阐 玉英, et al. 喘息型支气管肺炎儿血清肿瘤坏死因子、白细胞介素8与病因、病程的关系. 实用儿科临床杂志. 2000;15(2):83–84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-515X.2000.02.011. - DOI
-
- 郁 志伟, 钱 俊, 顾 晓虹, et al. 婴幼儿喘息性社区获得性肺炎患儿血清炎症因子的变化. http://www.zgddek.com/CN/abstract/abstract13716.shtml 中国当代儿科杂志. 2015;17(8):815–818. - PubMed
-
- Nayak A, Dodagatta-Marri E, Tsolaki AG, et al. An insight into the diverse roles of surfactant proteins, SP-A and SP-D in innate and adaptive immunity. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/OAPaper/oai_pubmedcentral.nih.gov_3369187. Front Immunol. 2012;3(5):1–21. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials