Distinct roles for the complement regulators factor H and Crry in protection of the kidney from injury
- PMID: 27165610
- PMCID: PMC4912413
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.036
Distinct roles for the complement regulators factor H and Crry in protection of the kidney from injury
Abstract
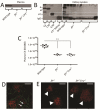
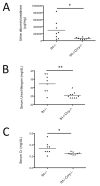
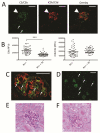
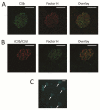
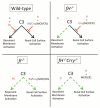
Mutations in the complement regulatory proteins are associated with several different diseases. Although these mutations cause dysregulated alternative pathway activation throughout the body, the kidneys are the most common site of injury. The susceptibility of the kidney to alternative pathway-mediated injury may be due to limited expression of complement regulatory proteins on several tissue surfaces within the kidney. To examine the roles of the complement regulatory proteins factor H and Crry in protecting distinct renal surfaces from alternative pathway mediated injury, we generated mice with targeted deletions of the genes for both proteins. Surprisingly, mice with combined genetic deletions of factor H and Crry developed significantly milder renal injury than mice deficient in only factor H. Deficiency of both factor H and Crry was associated with C3 deposition at multiple locations within the kidney, but glomerular C3 deposition was lower than that in factor H alone deficient mice. Thus, factor H and Crry are critical for regulating complement activation at distinct anatomic sites within the kidney. However, widespread activation of the alternative pathway reduces injury by depleting the pool of C3 available at any 1 location.
Keywords: complement; glomerulonephritis; inflammation.
Copyright © 2016 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Zipfel PF, Skerka C. Complement regulators and inhibitory proteins. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9:729–740. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

