Trends in suicidal behaviour in Dutch general practice 1983-2013: a retrospective observational study
- PMID: 27165647
- PMCID: PMC4874133
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2015-010868
Trends in suicidal behaviour in Dutch general practice 1983-2013: a retrospective observational study
Abstract
Objectives: To analyse trends in suicidal behaviour as reported by the Dutch sentinel general practices from 1983 to 2013. Second, to examine the relationship between suicidal behaviour and several patient characteristics. Finally, to compare the relationship between suicidal behaviour and patient characteristics before (1983-2007) and after (2008-2013) the start of the crisis.
Setting: 40 general practices in the Netherlands during the period 1983-2013.
Participants: Patients with an ICPC code of P77 (suicide attempt).
Primary and secondary outcomes: Primary outcomes were age-adjusted and gender-specific trends in reported suicides (342) and suicide attempts (1614). Secondary outcomes were the relationship between suicidal behaviour and age, household composition, history of depression, recognition of suicide ideation, treatment before the suicidal behaviour and contact within the past month before suicidal behaviour for the period 1983-2013. Additionally, separate frequencies for the periods 1983-2007 and 2008-2013 were presented.
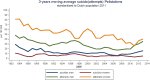
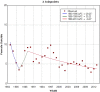
Results: Join-point analyses revealed a significant rise in male suicides from 2008 (b=0.32, SE=0.1, p=0.008), and an increase in male suicide attempts since 2009 (b=0.19, SE=0.04, p<0.001). Female suicidal behaviour showed a steady decrease from 1989 to 2013(b=-0.03, SE=0.007, p<0.0001 for female suicide, b=-0.02, SE=0.002, p<0.001 for female attempts). Before 2007, a history of depression was reported in 65% (168/257) of the suicides. After the start of the recession, a depression was recognised in 44% (22/50) of the patients who died by suicide.
Conclusions: Since 2008, there was a rise in the male suicide rate while female suicide behaviour has continued to decline. General practitioners less often reported a history of depression within patients who died due to suicide after 2007 than before. Training in the early recognition of suicide ideation in depressive patients might improve suicide prevention in primary care.
Keywords: EPIDEMIOLOGY; PRIMARY CARE.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://www.bmj.com/company/products-services/rights-and-licensing/
Figures
References
-
- O'Connor RC. Towards an integrated motivational–volitional model of suicidal behaviour. In: O'Connor RC, Platt S, Gordon J, eds. International handbook of suicide prevention: research, policy and practice. West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons, 2011:181–98.
-
- Hegerl U, Rummel-Kluge C, Värnik A et al. . Alliances against Depression–a community based approach to target depression and to prevent suicidal behaviour. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2013:37:2404–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous