Ligand trap for the activin type IIA receptor protects against vascular disease and renal fibrosis in mice with chronic kidney disease
- PMID: 27165838
- PMCID: PMC4868771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.002
Ligand trap for the activin type IIA receptor protects against vascular disease and renal fibrosis in mice with chronic kidney disease
Abstract
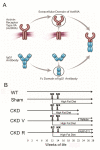
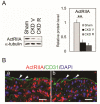
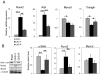
The causes of cardiovascular mortality associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD) are partly attributed to the CKD-mineral bone disorder (CKD-MBD). The causes of the early CKD-MBD are not well known. Our discovery of Wnt (portmanteau of wingless and int) inhibitors, especially Dickkopf 1, produced during renal repair as participating in the pathogenesis of the vascular and skeletal components of the CKD-MBD implied that additional pathogenic factors are critical. In the search for such factors, we studied the effects of activin receptor type IIA (ActRIIA) signaling by using a ligand trap for the receptor, RAP-011 (a soluble extracellular domain of ActRIIA fused to a murine IgG-Fc fragment). In a mouse model of CKD that stimulated atherosclerotic calcification, RAP-011 significantly increased aortic ActRIIA signaling assessed by the levels of phosphorylated Smad2/3. Furthermore, RAP-011 treatment significantly reversed CKD-induced vascular smooth muscle dedifferentiation as assessed by smooth muscle 22α levels, osteoblastic transition, and neointimal plaque calcification. In the diseased kidneys, RAP-011 significantly stimulated αklotho levels and it inhibited ActRIIA signaling and decreased renal fibrosis and proteinuria. RAP-011 treatment significantly decreased both renal and circulating Dickkopf 1 levels, showing that Wnt activation was downstream of ActRIIA. Thus, ActRIIA signaling in CKD contributes to the CKD-MBD and renal fibrosis. ActRIIA signaling may be a potential therapeutic target in CKD.
Keywords: chronic kidney disease; fibrosis; signaling; vascular calcification.
Copyright © 2016 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

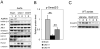
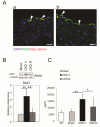

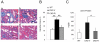
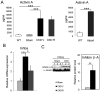
Comment in
-
Activin receptor IIA ligand trap in chronic kidney disease: 1 drug to prevent 2 complications-or even more?Kidney Int. 2016 Jun;89(6):1180-2. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2016.02.006. Kidney Int. 2016. PMID: 27181771
References
-
- Sarnak MJ, Levey AS, Schoolwerth AC, et al. Kidney Disease as a Risk Factor for Development of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation. 2003;108:2154–2169. - PubMed
-
- Papademetriou V, Lovato L, Doumas M, et al. Chronic kidney disease and intensive glycemic control increase cardiovascular risk in patients with type 2 diabetes. Kidney Int. 2015;87:649–659. - PubMed
-
- Pletcher MJ, Tice JA, Pignone M, et al. Using the Coronary Artery Calcium Score to Predict Coronary Heart Disease Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164:1285–1292. - PubMed
-
- Wexler L, Brundage B, Crouse J, et al. Coronary artery calcification: Pathophysiology, epidemiology, imaging methods, and clinical implications. Circulation. 1996;94:1175–1192. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

