From radioimmunoassay to mass spectrometry: a new method to quantify orexin-A (hypocretin-1) in cerebrospinal fluid
- PMID: 27165941
- PMCID: PMC4863245
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25162
From radioimmunoassay to mass spectrometry: a new method to quantify orexin-A (hypocretin-1) in cerebrospinal fluid
Abstract
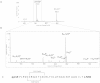
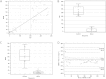
I(125) radioimmunoassay (RIA) is currently the standard technique for quantifying cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) orexin-A/hypocretin-1, a biomarker used to diagnose narcolepsy type 1. However, orexin-A RIA is liable to undergo cross-reactions with matrix constituents generating interference, high variability between batches, low precision and accuracy, and requires special radioactivity precautions. Here we developed the first quantitative mass spectrometry assay of orexin-A based on a multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) approach. This method was tested in keeping with the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI) guidelines and its clinical relevance was confirmed by comparing patients with narcolepsy type 1 versus patients with other neurological conditions. The results obtained using MRM and RIA methods were highly correlated, and Bland-Altman analysis established their interchangeability. However, the MRM values had a wider distribution and were 2.5 time lower than the RIA findings. In conclusion, this method of assay provides a useful alternative to RIA to quantify orexin-A, and may well replace it not only in narcolepsy type 1, but also in the increasing number of pathologies in which the quantification of this analyte is relevant.
Figures

References
-
- Sakurai T. et al.. Orexins and orexin receptors: a family of hypothalamic neuropeptides and G protein-coupled receptors that regulate feeding behavior. Cell 92, 1 page following 696 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Horvath T. L. et al.. Hypocretin (orexin) activation and synaptic innervation of the locus coeruleus noradrenergic system. The Journal of comparative neurology 415, 145–159 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

