Radiodermatitis after spinal arteriovenous fistula embolisation
- PMID: 27166008
- PMCID: PMC4885348
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2016-214384
Radiodermatitis after spinal arteriovenous fistula embolisation
Abstract
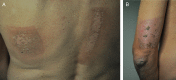
We report acute radiation dermatitis on a patient's back and left arm, which developed 4 weeks after endovascular embolisation of a spinal arteriovenous malformation. Vesciculation and erosions were followed by a gradual re-epithelisation of the skin resulting in rectangular hyperpigmented patches that resolved almost completely within 1 month. Fluoroscopic radiodermatitis has been reported with more frequency over the past decades because of the rise in duration and number of procedures performed under fluoroscopic guidance. Articles concerning this issue are mostly limited to case reports after coronary interventions, renal artery catheterisations, transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt procedures and embolisations of intracranial arteriovenous malformation. To the best of our knowledge, only two cases of radiation dermatitis after spinal arteriovenous malformation embolisation have been reported to date.
2016 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Dandurand M, Huet P, Guillot B. Secondary radiodermatitis caused by endovascular explorations: 5 cases. Ann Dermatol Venereol 1999;126:413–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous