Interaction of human biliverdin reductase with Akt/protein kinase B and phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase 1 regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 activity: a novel mechanism of Akt activation
- PMID: 27166089
- PMCID: PMC4970609
- DOI: 10.1096/fj.201600330RR
Interaction of human biliverdin reductase with Akt/protein kinase B and phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase 1 regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 activity: a novel mechanism of Akt activation
Abstract
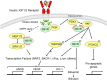
Biliverdin reductase A (BVR) and Akt isozymes have overlapping pleiotropic functions in the insulin/PI3K/MAPK pathway. Human BVR (hBVR) also reduces the hemeoxygenase activity product biliverdin to bilirubin and is directly activated by insulin receptor kinase (IRK). Akt isoenzymes (Akt1-3) are downstream of IRK and are activated by phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) phosphorylating T(308) before S(473) autophosphorylation. Akt (RxRxxSF) and PDK1 (RFxFPxFS) binding motifs are present in hBVR. Phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) isoforms α/β by Akts inhibits their activity; nonphosphorylated GSK3β inhibits activation of various genes. We examined the role of hBVR in PDK1/Akt1/GSK3 signaling and Akt1 in hBVR phosphorylation. hBVR activates phosphorylation of Akt1 at S(473) independent of hBVR's kinase competency. hBVR and Akt1 coimmunoprecipitated, and in-cell Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) and glutathione S-transferase pulldown analyses identified Akt1 pleckstrin homology domain as the interactive domain. hBVR activates phosphorylation of Akt1 at S(473) independent of hBVR's kinase competency. Site-directed mutagenesis, mass spectrometry, and kinetic analyses identified S(230) in hBVR (225)RNRYLSF sequence as the Akt1 target. Underlined amino acids are the essential residues of the signaling motifs. In cells, hBVR-activated Akt1 increased both GSK3α/β and forkhead box of the O class transcription class 3 (FoxO3) phosphorylation and inhibited total GSK3 activity; depletion of hBVR released inhibition and stimulated glucose uptake. Immunoprecipitation analysis showed that PDK1 and hBVR interact through hBVR's PDK1 binding (161)RFGFPAFS motif and formation of the PDK1/hBVR/Akt1 complex. sihBVR blocked complex formation. Findings identify hBVR as a previously unknown coactivator of Akt1 and as a key mediator of Akt1/GSK3 pathway, as well as define a key role for hBVR in Akt1 activation by PDK1.-Miralem, T., Lerner-Marmarosh, N., Gibbs, P. E. M., Jenkins, J. L., Heimiller, C., Maines, M. D. Interaction of human biliverdin reductase with Akt/protein kinase B and phosphatidylinositol-dependent kinase 1 regulates glycogen synthase kinase 3 activity: a novel mechanism of Akt activation.
Keywords: Akt/hBVR/GSK3 axis; activation of hBVR; bilirubin; heme oxygenase 1.
© FASEB.
Figures






References
-
- Kutty R. K., Maines M. D. (1981) Purification and characterization of biliverdin reductase from rat liver. J. Biol. Chem. 256, 3956–3962 - PubMed
-
- Maines M. D., Trakshel G. M. (1993) Purification and characterization of human biliverdin reductase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 300, 320–326 - PubMed
-
- Maines M. D., Trakshel G. M., Kutty R. K. (1986) Characterization of two constitutive forms of rat liver microsomal heme oxygenase. Only one molecular species of the enzyme is inducible. J. Biol. Chem. 261, 411–419 - PubMed
-
- Stocker R., Yamamoto Y., McDonagh A. F., Glazer A. N., Ames B. N. (1987) Bilirubin is an antioxidant of possible physiological importance. Science 235, 1043–1046 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

