Phytochemicals and botanical extracts regulate NF-κB and Nrf2/ARE reporter activities in DI TNC1 astrocytes
- PMID: 27166148
- PMCID: PMC4900906
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.05.004
Phytochemicals and botanical extracts regulate NF-κB and Nrf2/ARE reporter activities in DI TNC1 astrocytes
Abstract
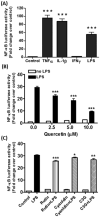
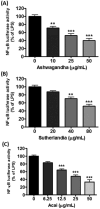
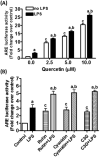
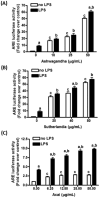
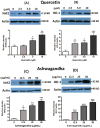
The increase in oxidative stress and inflammatory responses associated with neurodegenerative diseases has drawn considerable attention towards understanding the transcriptional signaling pathways involving NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells) and Nrf2 (Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-like 2). Our recent studies with immortalized murine microglial cells (BV-2) demonstrated effects of botanical polyphenols to inhibit lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nitric oxide (NO) and enhance Nrf2-mediated antioxidant responses (Sun et al., 2015). In this study, an immortalized rat astrocyte (DI TNC1) cell line expressing a luciferase reporter driven by the NF-κB or the Nrf2/Antioxidant Response Element (ARE) promoter was used to assess regulation of these two pathways by phytochemicals such as quercetin, rutin, cyanidin, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, as well as botanical extracts from Withania somnifera (Ashwagandha), Sutherlandia frutescens (Sutherlandia) and Euterpe oleracea (Açaí). Quercetin effectively inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB reporter activity and stimulated Nrf2/ARE reporter activity in DI TNC1 astrocytes. Cyanidin and the glycosides showed similar effects but only at much higher concentrations. All three botanical extracts effectively inhibited LPS-induced NF-κB reporter activity. These extracts were capable of enhancing ARE activity by themselves and further enhanced ARE activity in the presence of LPS. Quercetin and botanical extracts induced Nrf2 and HO-1 protein expression. Interestingly, Ashwagandha extract was more active in inducing Nrf2 and HO-1 expression in DI TNC1 astrocytes as compared to Sutherlandia and Açaí extracts. In summary, this study demonstrated NF-kB and Nrf2/ARE promoter activities in DI TNC1 astrocytes, and further showed differences in ability for specific botanical polyphenols and extracts to down-regulate LPS-induced NF-kB and up-regulate the NRF2/ARE activities in these cells.
Keywords: ARE reporter; Ashwagandha; Açaí; NF-κB reporter; Quercetin; Sutherlandia.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Abraham NG, Kappas A. Pharmacological and clinical aspects of heme oxygenase. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:79–127. - PubMed
-
- Cardozo LF, Pedruzzi LM, Stenvinkel P, Stockler-Pinto MB, Daleprane JB, Leite M, Jr, Mafra D. Nutritional strategies to modulate inflammation and oxidative stress pathways via activation of the master antioxidant switch Nrf2. Biochimie. 2013;95:1525–1533. - PubMed
-
- Chen JC, Ho FM, Pei-Dawn Lee C, Chen CP, Jeng KC, Hsu HB, Lee ST, Wen Tung W, Lin WW. Inhibition of iNOS gene expression by quercetin is mediated by the inhibition of IkappaB kinase, nuclear factor-kappa B and STAT1, and depends on heme oxygenase-1 induction in mouse BV-2 microglia. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;521:9–20. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

