Rational engineering of the Neurospora VS ribozyme to allow substrate recognition via different kissing-loop interactions
- PMID: 27166370
- PMCID: PMC5001590
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkw401
Rational engineering of the Neurospora VS ribozyme to allow substrate recognition via different kissing-loop interactions
Abstract
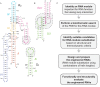
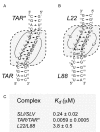
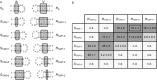
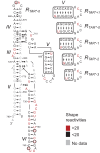
The Neurospora VS ribozyme is a catalytic RNA that has the unique ability to specifically recognize and cleave a stem-loop substrate through formation of a highly stable kissing-loop interaction (KLI). In order to explore the engineering potential of the VS ribozyme to cleave alternate substrates, we substituted the wild-type KLI by other known KLIs using an innovative engineering method that combines rational and combinatorial approaches. A bioinformatic search of the protein data bank was initially performed to identify KLIs that are structurally similar to the one found in the VS ribozyme. Next, substrate/ribozyme (S/R) pairs that incorporate these alternative KLIs were kinetically and structurally characterized. Interestingly, several of the resulting S/R pairs allowed substrate cleavage with substantial catalytic efficiency, although with reduced activity compared to the reference S/R pair. Overall, this study describes an innovative approach for RNA engineering and establishes that the KLI of the trans VS ribozyme can be adapted to cleave other folded RNA substrates.
© The Author(s) 2016. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Lilley D.M. Catalysis by the nucleolytic ribozymes. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011;39:641–646. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

