Bystander killing effect of DS-8201a, a novel anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 antibody-drug conjugate, in tumors with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterogeneity
- PMID: 27166974
- PMCID: PMC4946713
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.12966
Bystander killing effect of DS-8201a, a novel anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 antibody-drug conjugate, in tumors with human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 heterogeneity
Abstract
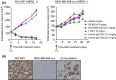
Antibody-drug conjugates deliver anticancer agents selectively and efficiently to tumor tissue and have significant antitumor efficacy with a wide therapeutic window. DS-8201a is a human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-targeting antibody-drug conjugate prepared using a novel linker-payload system with a potent topoisomerase I inhibitor, exatecan derivative (DX-8951 derivative, DXd). It was effective against trastuzumab emtansine (T-DM1)-insensitive patient-derived xenograft models with both high and low HER2 expression. In this study, the bystander killing effect of DS-8201a was evaluated and compared with that of T-DM1. We confirmed that the payload of DS-8201a, DXd (1), was highly membrane-permeable whereas that of T-DM1, Lys-SMCC-DM1, had a low level of permeability. Under a coculture condition of HER2-positive KPL-4 cells and negative MDA-MB-468 cells in vitro, DS-8201a killed both cells, whereas T-DM1 and an antibody-drug conjugate with a low permeable payload, anti-HER2-DXd (2), did not. In vivo evaluation was carried out using mice inoculated with a mixture of HER2-positive NCI-N87 cells and HER2-negative MDA-MB-468-Luc cells by using an in vivo imaging system. In vivo, DS-8201a reduced the luciferase signal of the mice, indicating suppression of the MDA-MB-468-Luc population; however, T-DM1 and anti-HER2-DXd (2) did not. Furthermore, it was confirmed that DS-8201a was not effective against MDA-MB-468-Luc tumors inoculated at the opposite side of the NCI-N87 tumor, suggesting that the bystander killing effect of DS-8201a is observed only in cells neighboring HER2-positive cells, indicating low concern in terms of systemic toxicity. These results indicated that DS-8201a has a potent bystander effect due to a highly membrane-permeable payload and is beneficial in treating tumors with HER2 heterogeneity that are unresponsive to T-DM1.
Keywords: Antibody-drug conjugate; HER2; T-DM; bystander killing; topoisomerase I inhibitor.
© 2016 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures




References
-
- Bross PF, Beitz J, Chen G et al Approval summary: gemtuzumab ozogamicin in relapsed acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2001; 7: 1490–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

