Double mutant P53 (N340Q/L344R) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through upregulation of Pim1 mediated by PKM2 and LncRNA CUDR
- PMID: 27167190
- PMCID: PMC5341818
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.9089
Double mutant P53 (N340Q/L344R) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through upregulation of Pim1 mediated by PKM2 and LncRNA CUDR
Abstract
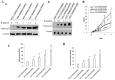
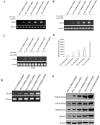
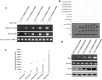
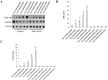
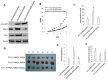
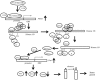
P53 is frequently mutated in human tumors as a novel gain-of-function to promote tumor development. Although dimeric (M340Q/L344R) influences on tetramerisation on site-specific post-translational modifications of p53, it is not clear how dimeric (M340Q/L344R) plays a role during hepatocarcinogenesis. Herein, we reveal that P53 (N340Q/L344R) promotes hepatocarcinogenesis through upregulation of PKM2. Mechanistically, P53 (N340Q/L344R) forms complex with CUDR and the complex binds to the promoter regions of PKM2 which enhances the expression, phosphorylation of PKM2 and its polymer formation. Thereby, the polymer PKM2 (tetramer) binds to the eleventh threonine on histone H3 that increases the phosphorylation of the eleventh threonine on histone H3 (pH3T11). Furthermore, pH3T11 blocks HDAC3 binding to H3K9Ac that prevents H3K9Ac from deacetylation and stabilizes the H3K9Ac modification. On the other hand, it also decreased tri-methylation of histone H3 on the ninth lysine (H3K9me3) and increases one methylation of histone H3 on the ninth lysine (H3K9me1). Moreover, the combination of H3K9me1 and HP1 α forms more H3K9me3-HP1α complex which binds to the promoter region of Pim1, enhancing the expression of Pim1 that enhances the expression of TERT, oncogenic lncRNA HOTAIR and reduces the TERRA expression. Ultimately, P53 (N340Q/L344R) accerlerates the growth of liver cancer cells Hep3B by activating telomerase and prolonging telomere through the cascade of P53 (N340Q/L344R)-CUDR-PKM2-pH3T11- (H3K9me1-HP1α)-Pim1- (TERT-HOTAIR-TERRA). Understanding the novel functions of P53 (N340Q/L344R) will help in the development of new liver cancer therapeutic approaches that may be useful in a broad range of cancer types.
Keywords: LncRNA CUDR; PKM2; hepatoma; mutant P53 (N340Q/L344R).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Figures


References
-
- Greenblatt MS, Feitelson MA, Zhu M, Bennett WP, Welsh JA, Jones R, Borkowski A, Harris CC. Integrity of p53 in hepatitis B x antigen-positive and -negative hepatocellular carcinomas. Cancer Res. 1997;57:426–32. - PubMed
-
- Feitelson MA, Zhu M, Duan LX, London WT. patitis B x antigen and p53 are associated in vitro and in liver tissues from patients with primary hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 1993;8:1109–17. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

