EPID based in vivo dosimetry system: clinical experience and results
- PMID: 27167283
- PMCID: PMC5690938
- DOI: 10.1120/jacmp.v17i3.6070
EPID based in vivo dosimetry system: clinical experience and results
Abstract
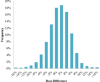
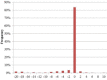
Mandatory in several countries, in vivo dosimetry has been recognized as one of the next milestones in radiation oncology. Our department has implemented clinically an EPID based in vivo dosimetry system, EPIgray, by DOSISOFT S.A., since 2006. An analysis of the measurements per linac and energy over a two-year period was performed, which included a more detailed examination per technique and treat-ment site over a six-month period. A comparison of the treatment planning system doses and the doses estimated by EPIgray shows a mean of the differences of 1.9% (± 5.2%) for the two-year period. The 3D conformal treatment plans had a mean dose difference of 2.0% (± 4.9%), while for intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapy treatments the mean dose difference was -3.0 (± 5.3%) and -2.5 (± 5.2%), respectively. In addition, root cause analyses were conducted on the in vivo dosimetry measurements of two breast cancer treatment techniques, as well as prostate treatments with intensity-modulated radiotherapy and volumetric-modulated arc therapy. During the breast study, the dose differences of breast treatments in supine position were correlated to patient setup and EPID positioning errors. Based on these observations, an automatic image shift correc-tion algorithm is developed by DOSIsoft S.A. The prostate study revealed that beams and arcs with out-of-tolerance in vivo dosimetry results tend to have more complex modulation and a lower exposure of the points of interest. The statistical studies indicate that in vivo dosimetry with EPIgray has been successfully imple-mented for classical and complex techniques in clinical routine at our institution. The additional breast and prostate studies exhibit the prospects of EPIgray as an easy supplementary quality assurance tool. The validation, the automatization, and the reduction of false-positive results represent an important step toward adaptive radiotherapy with EPIgray.
Figures





References
-
- American Association of Physicists in Medicine . Diode in vivo dosimetry for patients receiving external beam radiation therapy. AAPM report No. 87. Report of the Radiation Therapy Committee, Task Group 62. Madison, WI: Medical Physics Publishing; 2005.
-
- International Atomic Energy Agency . Development of procedures for in vivo dosimetry in radiotherapy [Electronic version]. IAEA Human Health Report No. 8. Vienna, Austria: International Atomic Energy Agency; 2013. Accessed 2015 Jan. Available from: http://www‐pub.iaea.org/MTCD/Publications/PDF/Pub1606_web.pdf
-
- Kutcher, GJ , Coia, L , Gillin, M , et al. Comprehensive QA for radiation oncology: report of AAPM Radiation Therapy Committee Task Group 40. Med Phys. 1994; 21(4):581–618. - PubMed
-
- British Institute of Radiology, Institute of Physics and Engineering in Medicine, Society and College of Radiographers, The Royal College of Radiologists . Implementing in vivo dosimetry [Internet]. London: Royal College of Radiologists; 2008. Accessed 2015 Jan. Available from: https://www.rcr.ac.uk/docs/oncology/pdf/Invivo_joint.pdf
-
- Mijnheer B, Beddar S, Izewska J, Reft C. In vivo dosimetry in external beam radiotherapy [Electronic version]. Med Phys. 2013;40(7):070903. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

