A voltammetric and mathematical analysis of histaminergic modulation of serotonin in the mouse hypothalamus
- PMID: 27167463
- PMCID: PMC7279509
- DOI: 10.1111/jnc.13659
A voltammetric and mathematical analysis of histaminergic modulation of serotonin in the mouse hypothalamus
Abstract
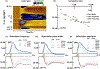
Histamine and serotonin are neuromodulators which facilitate numerous, diverse neurological functions. Being co-localized in many brain regions, these two neurotransmitters are thought to modulate one another's chemistry and are often implicated in the etiology of disease. Thus, it is desirable to interpret the in vivo chemistry underlying neurotransmission of these two molecules to better define their roles in health and disease. In this work, we describe a voltammetric approach to monitoring serotonin and histamine simultaneously in real time. Via electrical stimulation of the axonal bundles in the medial forebrain bundle, histamine release was evoked in the mouse premammillary nucleus. We found that histamine release was accompanied by a rapid, potent inhibition of serotonin in a concentration-dependent manner. We developed mathematical models to capture the experimental time courses of histamine and serotonin, which necessitated incorporation of an inhibitory receptor on serotonin neurons. We employed pharmacological experiments to verify that this serotonin inhibition was mediated by H3 receptors. Our novel approach provides fundamental mechanistic insights that can be used to examine the full extent of interconnectivity between histamine and serotonin in the brain. Histamine and serotonin are co-implicated in many of the brain's functions. In this paper, we develop a novel voltammetric method for simultaneous real-time monitoring of histamine and serotonin in the mouse premammillary nucleus. Electrical stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle evokes histamine and inhibits serotonin release. We show voltammetrically, mathematically, and pharmacologically that this serotonin inhibition is H3 receptor mediated.
Keywords: H3 autoreceptor; carbon fiber microelectrodes; fast-scan cyclic voltammetry; heteroreceptor; thioperamide.
© 2016 International Society for Neurochemistry.
Figures



References
-
- Akhtar M, Pillai KK and Vohora D (2005) Effect of thioperamide on modified forced swimming test-induced oxidative stress in mice. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol 97, 218–221. - PubMed
-
- Auvinen S and Panula P (1988) Development of histamineimmunoreactive neurons in the rat brain. J. Comp. Neurol 276, 289–303. - PubMed
-
- Bernaerts P, Lamberty Y and Tirelli E (2004) Histamine H3 antagonist thioperamide dose-dependently enhances memory consolidation and reverses amnesia induced by dizocilpine or scopolamine in a one-trial inhibitory avoidance task in mice. Behav. Brain Res 154, 211–219. - PubMed
-
- Bordi F, Mor M, Plazzi PV, Silva C, Caretta A and Morini G (1992) HPLC detection of thioperamide from biological samples and its determination in rat blood and brain after systemic administration. Farmaco, 47, 1095–1103. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

