0.5-keV Soft X-ray attosecond continua
- PMID: 27167525
- PMCID: PMC4865833
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11493
0.5-keV Soft X-ray attosecond continua
Abstract
Attosecond light pulses in the extreme ultraviolet have drawn a great deal of attention due to their ability to interrogate electronic dynamics in real time. Nevertheless, to follow charge dynamics and excitations in materials, element selectivity is a prerequisite, which demands such pulses in the soft X-ray region, above 200 eV, to simultaneously cover several fundamental absorption edges of the constituents of the materials. Here, we experimentally demonstrate the exploitation of a transient phase matching regime to generate carrier envelope controlled soft X-ray supercontinua with pulse energies up to 2.9±0.1 pJ and a flux of (7.3±0.1) × 10(7) photons per second across the entire water window and attosecond pulses with 13 as transform limit. Our results herald attosecond science at the fundamental absorption edges of matter by bridging the gap between ultrafast temporal resolution and element specific probing.
Figures
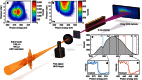
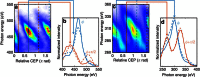
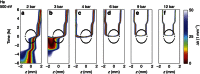
References
-
- Krausz F. & Ivanov M. Y. Attosecond physics. Rev. Mod. Phys. 81, 163–23497 (2009).
-
- Belshaw L. et al.. Observation of ultrafast charge migration in an amino acid. Phys. Chem. Lett. 3, 3751–3754 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Schiffrin A. et al.. Optical-field-induced current in dielectrics. Nature 493, 70–74 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Kling M. F. et al.. Control of electron localization in molecular dissociation. Science 312, 246–248 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Sansone G. et al.. Electron localization following attosecond molecular photoionization. Nature 465, 763–766 (2010). - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

