Association of polymorphisms at the microRNA binding site of the caprine KITLG 3'-UTR with litter size
- PMID: 27168023
- PMCID: PMC4863368
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25691
Association of polymorphisms at the microRNA binding site of the caprine KITLG 3'-UTR with litter size
Abstract
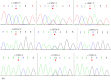
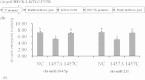
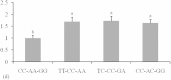
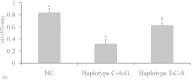
This study identified three novel single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) (c.1389C > T, c.1457A > C and c.1520G > A) in the caprine KITLG 3'-UTR through DNA sequencing. The three SNP loci were closely linked in Guanzhong dairy (GD) goats. Two alleles of the c.1457A > C SNP introduced two miRNA sites (chi-miR-204-5p and chi-miR-211). Individuals with combined genotype TT-CC-AA had a higher litter size compared with those with combined genotypes CC-AA-GG, TC-CC-GA and CC-AC-GG (P < 0.05). Luciferase assays showed that chi-miR-204-5p and chi-miR-211 suppressed luciferase expression in the presence of allele 1457A compared with negative control (NC) and allele 1457C (P < 0.05). Western blot revealed that KITLG significantly decreased in the granulosa cells (GCs) of genotype AA compared with that in the GCs of genotype CC and NC (P < 0.05). The KITLG mRNA levels of the CC-AA-GG carriers significantly decreased compared with those of the TT-CC-AA, TC-CC-GA and CC-AC-GG carriers. In addition, cell proliferation was reduced in haplotype C-A-G GCs compared with that in haplotype T-C-A GCs. These results suggest that SNPs c.1389C > T, c.1457A > C and c.1520G > A account for differences in the litter size of GD goats because chi-miR-204-5p and chi-miR-211 could change the expression levels of the KITLG gene and reduce GC proliferation.
Figures
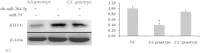
Similar articles
-
Association analysis between variants in KITLG gene and litter size in goats.Gene. 2015 Mar 1;558(1):126-30. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2014.12.058. Epub 2014 Dec 27. Gene. 2015. PMID: 25550049
-
Two mutations in the 5'-flanking region of the KITLG gene are associated with litter size of dairy goats.Anim Genet. 2015 Jun;46(3):308-11. doi: 10.1111/age.12277. Epub 2015 Mar 18. Anim Genet. 2015. PMID: 25786329
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphisms g.151435C>T and g.173057T>C in PRLR gene regulated by bta-miR-302a are associated with litter size in goats.Theriogenology. 2015 Jun;83(9):1477-1483.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.theriogenology.2015.01.030. Epub 2015 Jan 31. Theriogenology. 2015. PMID: 25799469
-
Polymorphisms of caprine POU1F1 gene and their association with litter size in Jining Grey goats.Mol Biol Rep. 2012 Apr;39(4):4029-38. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-1184-5. Epub 2011 Jul 17. Mol Biol Rep. 2012. PMID: 21769479
-
Two Mutations in the Caprine MTHFR 3'UTR Regulated by MicroRNAs Are Associated with Milk Production Traits.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 17;10(7):e0133015. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133015. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26186555 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Identification of Functional Variants Between Tong Sheep and Hu Sheep by Whole-Genome Sequencing Pools of Individuals.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 30;25(23):12919. doi: 10.3390/ijms252312919. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39684630 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of novel polymorphism in buffalo stanniocalcin-1 gene and its expression analysis in mammary gland under different stages of lactation.J Genet. 2019 Jun;98(2):38. J Genet. 2019. PMID: 31204715
-
A polymorphism in the 3'-untranslated region of the matrix metallopeptidase 9 gene is associated with susceptibility to idiopathic calcium nephrolithiasis in the Chinese population.J Int Med Res. 2020 Dec;48(12):300060520980211. doi: 10.1177/0300060520980211. J Int Med Res. 2020. PMID: 33345667 Free PMC article.
-
WNT5B regulates myogenesis and fiber type conversion by affecting mRNA stability.Int J Biol Sci. 2025 Jun 9;21(9):3934-3948. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.102309. eCollection 2025. Int J Biol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40612684 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Polymorphisms in Candidate Genes with the Litter Size in Two Sheep Breeds.Animals (Basel). 2019 Nov 12;9(11):958. doi: 10.3390/ani9110958. Animals (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31726757 Free PMC article.
References
-
- An X. P. et al.. Two mutations in the 5′-flanking region of the KITLG gene are associated with litter size of dairy goats. Anim. Genet. 46, 308–11 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Miyoshi T. et al.. Regulatory role of kit ligand-c-kit interaction and oocyte factors in steroidogenesis by rat granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 358, 18–26 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Rovasio R. A., Faas L. & Battiato N. L. Insights into Stem Cell Factor chemotactic guidance of neural crest cells revealed by a real-time directionality-based assay. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 91, 375–90 (2012). - PubMed
-
- Dong Y. et al.. Sequencing and automated whole-genome optical mapping of the genome of a domestic goat (Capra hircus). Nat. Biotechnol. 31, 135–41 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Driancourt M. A., Reynaud K., Cortvrindt R. & Smitz J. Roles of KIT and KIT LIGAND in ovarian function. Rev. Reprod. 5, 143–52 (2000). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

