Effects of Shenqi Fuzheng injection on Fas/FasL protein expression levels in the cardiomyocytes of a mouse model of viral myocarditis
- PMID: 27168814
- PMCID: PMC4840685
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2016.3165
Effects of Shenqi Fuzheng injection on Fas/FasL protein expression levels in the cardiomyocytes of a mouse model of viral myocarditis
Abstract
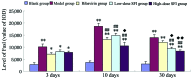
The aim of the present study was to examine the effects of Shenqi Fuzheng injection (SFI) on Fas and FasL protein expression levels in the cardiomyocytes of mice with viral myocarditis (VMC) and to explore the underlying anti-apoptotic mechanisms. A total of 120 male BALB/c mice were randomly divided into five groups as follows: Blank control group, model group, ribavirin group, low-dose SFI group and high-dose SFI group. The VMC model was established by the injection of coxsackievirus group B type 3 and saline, ribavirin or SFI was administered 30 min later. Cardiac samples were harvested from mice in each group on days 3, 10 and 30. Apoptosis of cardiac cells was examined using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick-end labeling, and Fas and FasL protein expression levels were detected using immunohistochemistry. Myocardial apoptosis and Fas/FasL protein expression levels were significantly increased in the model group, as compared with the blank group (P<0.01), whereas the apoptotic index (AI) and Fas/FasL protein expression levels of cardiac cells in the high-dose SFI group were significantly decreased compared with those in the model group on day 10 (acute phase; P<0.01). The AI and Fas/FasL protein expression levels of cardiac cells in the low- and high-dose SFI groups were also significantly decreased on day 30 (chronic phase; P<0.01); however, no differences between the high- and low-dose groups were detected. In conclusion, SFI relieves VMC via the downregulation of Fas and FasL protein expression and the inhibition of cell apoptosis.
Keywords: Chinese medicine; Fas/FasL protein; Shenqi Fuzheng injection; cell apoptosis; viral myocarditis.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
