Hepatocellular carcinoma and the risk of occupational exposure
- PMID: 27168870
- PMCID: PMC4858622
- DOI: 10.4254/wjh.v8.i13.573
Hepatocellular carcinoma and the risk of occupational exposure
Abstract
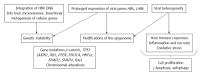
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common type of liver cancer. The main risk factors for HCC are alcoholism, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, obesity, type 2 diabetes, cirrhosis, aflatoxin, hemochromatosis, Wilson's disease and hemophilia. Occupational exposure to chemicals is another risk factor for HCC. Often the relationship between occupational risk and HCC is unclear and the reports are fragmented and inconsistent. This review aims to summarize the current knowledge regarding the association of infective and non-infective occupational risk exposure and HCC in order to encourage further research and draw attention to this global occupational public health problem.
Keywords: Arsenic; Autophagy; Cadmium; Chemical agents; Epigenetic events; Hepatitis B virus; Hepatitis C virus; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Mitophagy; Occupational exposure.
Figures
References
-
- Wallace MC, Preen D, Jeffrey GP, Adams LA. The evolving epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma: a global perspective. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;9:765–779. - PubMed
-
- Papatheodoridis GV, Chan HL, Hansen BE, Janssen HL, Lam-pertico P. Risk of hepatocellular carcinoma in chronic hepatitis B: assessment and modification with current antiviral therapy. J Hepatol. 2015;62:956–967. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources