Recurrence of the Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Burr-Hole Drainage with or without Intraoperative Saline Irrigation
- PMID: 27169042
- PMCID: PMC4852611
- DOI: 10.13004/kjnt.2014.10.2.101
Recurrence of the Chronic Subdural Hematoma after Burr-Hole Drainage with or without Intraoperative Saline Irrigation
Abstract
Objective: Although standard method has not been established for the chronic subdural hematoma (CSDH), burr-hole trephination and closed system drainage with or without irrigation has been widely accepted as the treatment of choice. The aim of this study is to analysis the post-operative recurrence rates after burr-hole trephination of the CSDH according to the conduction of irrigation.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed 184 patients with CSDH who underwent surgical treatment between January 2009 and December 2013. And 152 patients fulfilled the inclusion criteria as follows: 1) CSDH diagnosed on computed tomography (CT), 2) unilateral hematoma, 3) burr-hole trephination with closed system drainage, and 4) follow-up CT for at least 3 months. Those patients were divided into two groups. Group A (n=38) underwent burr-hole trephination without irrigation, and Group B (n=114), burr-hole trephination with saline irrigation.
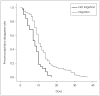
Results: The overall post-operative recurrence rate was 19.1% (n=29) in this study. The majority of recurrence showed in Group B. Twenty-eight patients (24.6%) of Group B had recurrence and only 1 patient (2.6%) of Group A showed recurrence. The recurrence rate was significantly higher in Group B compared with Group A (p=0.003). Another affecting factor for the recurrence was the amount of postoperative pneumocephalus (p=0.02). No catastrophic complications were found in postoperative course.
Conclusion: Although there was no difference of clinical outcome in both groups, the recurrence rate was higher in saline irrigation group compared with no irrigation group. We suggest that saline irrigation procedure be reserved only for selected cases in CSDH burr-hole surgery.
Keywords: Drainage; Hematoma subdural chronic; Pneumocephalus; Recurrence; Therapeutic irrigation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A comparative study of treatments for chronic subdural hematoma: burr hole drainage versus burr hole drainage with irrigation.Kurume Med J. 2011;58(1):35-9. doi: 10.2739/kurumemedj.58.35. Kurume Med J. 2011. PMID: 22027196 Clinical Trial.
-
Which surgical procedure is effective for refractory chronic subdural hematoma? Analysis of our surgical procedures and literature review.J Clin Neurosci. 2018 Mar;49:40-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jocn.2017.11.009. Epub 2017 Dec 20. J Clin Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 29274740 Review.
-
A comparative study of the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma--burr hole drainage versus burr hole irrigation.Surg Neurol. 2002 Jun;57(6):405-9; discussion 410. doi: 10.1016/s0090-3019(02)00720-6. Surg Neurol. 2002. PMID: 12176202
-
A randomized controlled trial comparing the outcome of burr-hole irrigation with and without drainage in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma: a preliminary report.World Neurosurg. 2011 May-Jun;75(5-6):731-6; discussion 620-3. doi: 10.1016/j.wneu.2010.11.042. World Neurosurg. 2011. PMID: 21704944 Clinical Trial.
-
Burr-hole Irrigation with Closed-system Drainage for the Treatment of Chronic Subdural Hematoma: A Meta-analysis.Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2016;56(2):62-8. doi: 10.2176/nmc.ra.2015-0013. Epub 2015 Sep 17. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2016. PMID: 26377830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Irrigation versus no irrigation in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of 1581 patients.Neurosurg Rev. 2024 Mar 28;47(1):130. doi: 10.1007/s10143-024-02368-2. Neurosurg Rev. 2024. PMID: 38538863
-
Half-Saline Versus Normal-Saline as Irrigation Solutions in Burr Hole Craniostomy to Treat Chronic Subdural Hematomata: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Korean J Neurotrauma. 2022 Sep 29;18(2):221-229. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2022.18.e47. eCollection 2022 Oct. Korean J Neurotrauma. 2022. PMID: 36381457 Free PMC article.
-
Finnish study of intraoperative irrigation versus drain alone after evacuation of chronic subdural haematoma (FINISH): a study protocol for a multicentre randomised controlled trial.BMJ Open. 2020 Jun 21;10(6):e038275. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-038275. BMJ Open. 2020. PMID: 32565480 Free PMC article.
-
Hemoglobin Concentration May Affect the Effect of Atorvastin on Chronic Subdural Hematoma After Burr-Hole Drainage at High Altitude.Front Neurosci. 2020 Jun 12;14:503. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.00503. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32595442 Free PMC article.
-
Randomized controlled study on the curative effects of twist-drill craniotomy and burr-hole craniotomy in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma.Exp Ther Med. 2018 Aug;16(2):959-965. doi: 10.3892/etm.2018.6265. Epub 2018 Jun 7. Exp Ther Med. 2018. PMID: 30116345 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aung TH, Wong WK, Mo HP, Tsang CS. Management of chronic subdural haematoma: burr hole drainage, replacement with Hartmann's solution, and closed-system drainage. Hong Kong Med J. 1999;5:383–386. - PubMed
-
- Camel M. Twist-drill craniostomy for the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2000;11:515–518. - PubMed
-
- Ducruet AF, Grobelny BT, Zacharia BE, Hickman ZL, DeRosa PL, Anderson K, et al. The surgical management of chronic subdural hematoma. Neurosurg Rev. 2012;35:155–169. discussion 169. - PubMed
-
- Erol FS, Topsakal C, Faik Ozveren M, Kaplan M, Tiftikci MT. Irrigation vs. closed drainage in the treatment of chronic subdural hematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2005;12:261–263. - PubMed
-
- Gurelik M, Aslan A, Gurelik B, Ozum U, Karadag O, Kars HZ. A safe and effective method for treatment of chronic subdural haematoma. Can J Neurol Sci. 2007;34:84–87. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

