Effects of a community-based salt reduction program in a regional Australian population
- PMID: 27169380
- PMCID: PMC4864903
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-016-3064-3
Effects of a community-based salt reduction program in a regional Australian population
Abstract
Background: Salt reduction is a public health priority but there are few studies testing the efficacy of plausible salt reduction programs.
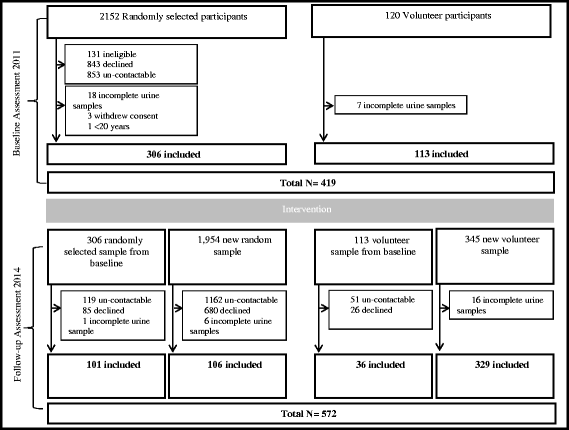
Methods: A multi-faceted, community-based salt reduction program using the Communication for Behavioral Impact framework was implemented in Lithgow, Australia. Single 24-h urine samples were obtained from 419 individuals at baseline (2011) and from 572 at follow-up (2014). Information about knowledge and behaviors relating to salt was also collected.
Results: Survey participants were on average 56 years old and 58 % female. Mean salt intake estimated from 24-h urine samples fell from 8.8 g/day (SD = 3.6 g/day) in 2011 to 8.0 (3.6) g/day in 2014 (-0.80, 95 % confidence interval -1.2 to -0.3;p < 0.001). There were significant increases in the proportion of participants that knew the recommended upper limit of salt intake (18 % vs. 29 %; p < 0.001), knew the importance of salt reduction (64 % vs. 78 %; p < 0.001) and reported changing their behaviors to reduce their salt intake by using spices (5 % vs. 28 %; p < 0.001) and avoiding eating out (21 % vs. 34 %; p < 0.001). However, the proportions that checked food labels (30 % vs. 25 %; p = 0.02) fell, as did the numbers avoiding processed foods (44 % vs. 35 %; p = 0.006). Twenty-six percent reported using salt substitute at the end of the intervention period and 90 % had heard about the program. Findings were robust to multivariable adjustment.
Conclusions: Implementation of this multi-faceted community-based program was associated with a ~10 % reduction in salt consumption in an Australian regional town. These findings highlight the potential of well-designed health promotion programs to compliment other population-based strategies to bring about much-needed reductions in salt consumption.
Clinical trial registration: NCT02105727 .
Keywords: 24-hour urine; Cardiovascular disease prevention; Salt; Sodium.
Figures

References
-
- Sacks FM, Svetkey LP, Vollmer WM, Appel LJ, Bray GA, Harsha D, Obarzanek E, Conlin PR, Miller ER, 3rd, Simons-Morton DG, et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. DASH-Sodium Collaborative Research Group. N Engl J Med. 2001;344(1):3–10. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200101043440101. - DOI - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Formal Meeting of Member States to Conclude the Work on the Comprehensive Global Monitoring Framework, Including Indicators, and a set of Voluntary Global Targets for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2012.
-
- Cook NR, Cutler JA, Obarzanek E, Buring JE, Rexrode KM, Kumanyika SK, Appel LJ, Whelton PK. Long term effects of dietary sodium reduction on cardiovascular disease outcomes: observational follow-up of the trials of hypertension prevention (TOHP) BMJ. 2007;334(7599):885–888. doi: 10.1136/bmj.39147.604896.55. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

