Trends in Acute Ischemic Stroke Hospitalizations in the United States
- PMID: 27169548
- PMCID: PMC4889194
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003233
Trends in Acute Ischemic Stroke Hospitalizations in the United States
Abstract
Background: Population-based studies have revealed declining acute ischemic stroke (AIS) hospitalization rates in the United States, but no study has assessed recent temporal trends in race/ethnic-, age-, and sex-specific AIS hospitalization rates.
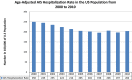
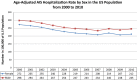
Methods and results: Temporal trends in hospitalization for AIS from 2000 to 2010 were assessed among adults ≥25 years using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample. Age-, sex-, and race/ethnic-specific and age-adjusted stroke hospitalization rates were calculated using the weighted number of hospitalizations and US census data. From 2000 to 2010, age-adjusted stroke hospitalization rates decreased from 250 to 204 per 100 000 (overall rate reduction 18.4%). Age-specific AIS hospitalization rates decreased for individuals aged 65 to 84 years (846 to 605 per 100 000) and ≥85 years (2077 to 1618 per 100 000), but increased for individuals aged 25 to 44 years (16 to 23 per 100 000) and 45 to 64 years (149 to 156 per 100 000). Blacks had the highest age-adjusted yearly hospitalization rates, followed by Hispanics and whites (358, 170, and 155 per 100 000 in 2010). Age-adjusted AIS hospitalization rates increased for blacks but decreased for Hispanics and whites. Age-adjusted AIS hospitalization rates were lower in women and declined more steeply compared to men (272 to 212 per 100 000 in women versus 298 to 245 per 100 000 in men).
Conclusions: Although overall stroke hospitalizations declined in the United States, the reduction was more pronounced among older individuals, women, Hispanics, and whites. Renewed efforts at targeting risk factor control among vulnerable individuals may be warranted.
Keywords: acute ischemic stroke; hospitalization; nationwide inpatient sample; stroke; trends.
© 2016 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures


Comment in
-
Rising Stroke Incidence in Young Adults: More Epidemiological Evidence, More Questions to Be Answered.J Am Heart Assoc. 2016 May 11;5(5):e003661. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.116.003661. J Am Heart Assoc. 2016. PMID: 27169549 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ovbiagele B. Nationwide trends in in‐hospital mortality among patients with stroke. Stroke. 2010;41:1748–1754. - PubMed
-
- Towfighi A, Ovbiagele B, Saver JL. Therapeutic milestone: stroke declines from the second to the third leading organ‐ and disease‐specific cause of death in the United States. Stroke. 2010;41:499–503. - PubMed
-
- Towfighi A, Saver JL. Stroke declines from third to fourth leading cause of death in the United States: historical perspective and challenges ahead. Stroke. 2011;42:2351–2355. - PubMed
-
- Ovbiagele B, Markovic D, Towfighi A. Recent age‐ and gender‐specific trends in mortality during stroke hospitalization in the United States. Int J Stroke. 2011;6:379–387. - PubMed
-
- Lee LK, Bateman BT, Wang S, Schumacher HC, Pile‐Spellman J, Saposnik G. Trends in the hospitalization of ischemic stroke in the United States, 1998–2007. Int J Stroke. 2012;7:195–201. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

