Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and heart failure in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and observational studies
- PMID: 27169565
- PMCID: PMC4863354
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-016-0260-0
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and heart failure in type 2 diabetes: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized and observational studies
Abstract
Background: The effect of glucagon-like peptide-1(GLP-1) receptor agonists on heart failure remains uncertain. We therefore conducted a systematic review to assess the possible impact of GLP-1 agonists on heart failure or hospitalization for heart failure in patients with type 2 diabetes.
Methods: We searched MEDLINE, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) and ClinicalTrials.gov to identify randomized controlled trials (RCTs) and observational studies that addressed the effect of GLP-1 receptor agonists in adults with type 2 diabetes, and explicitly reported heart failure or hospitalization for heart failure. Two paired reviewers screened reports, collected data, and assessed the risk of bias. We pooled data from RCTs and observational studies separately, and used the GRADE approach to rate the quality of evidence.
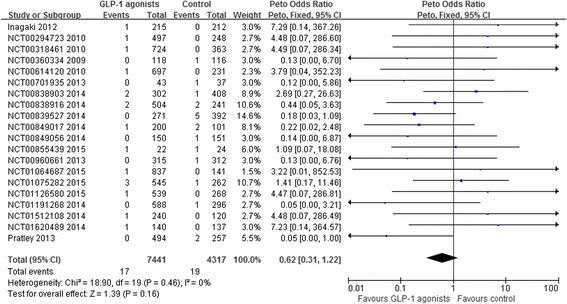
Results: We identified 25 studies that were eligible for our review; 21 RCTs (n = 18,270) and 4 observational studies (n = 111,029). Low quality evidence from 20 RCTs suggested, if anything, a lower incidence of heart failure between GLP-1 agonists versus control (17/7,441 vs. 19/4,317; odds ratio (OR) 0.62, 95 % confidence interval (CI) 0.31 to 1.22; risk difference (RD) 19 fewer, 95 % CI 34 fewer to 11 more per 1000 over 5 years). Three cohort studies comparing GLP-1 agonists to alternative agents provided very low quality evidence that GLP-1 agonists do not increase the incidence of heart failure. One RCT provided moderate quality evidence that GLP-1 agonists were not associated with hospitalization for heart failure (lixisenatide vs placebo: 122/3,034 vs. 127/3,034; adjusted hazard ratio 0.96, 95 % CI 0.75 to 1.23; RD 4 fewer, 95 % CI 25 fewer to 23 more per 1000 over 5 years) and a case-control study provided very low quality evidence also suggesting no association (GLP-1 agonists vs. other anti-hyperglycemic drugs: 1118 cases and 17,626 controls, adjusted OR 0.67, 95 % CI 0.32 to 1.42).
Conclusions: The current evidence suggests that GLP-1 agonists do not increase the risk of heart failure or hospitalization for heart failure among patients with type 2 diabetes.
Keywords: Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor; Heart failure; Meta-analysis; Systematic review; Type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous