Validating the Sensitivity of High-Resolution Melting Analysis for JAK2 V617F Mutation in the Clinical Setting
- PMID: 27169616
- PMCID: PMC6807203
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.21945
Validating the Sensitivity of High-Resolution Melting Analysis for JAK2 V617F Mutation in the Clinical Setting
Abstract
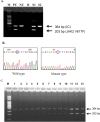
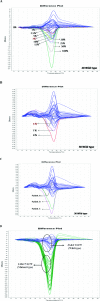
Background: Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) plays an important role in normal hematopoietic growth factor signaling. The detection of the JAK2 V617F mutation (c.1849GNT, GTC → TTC) is crucial for the diagnosis of myeloproliferative neoplasm (MPN) and has become the essential criteria for diagnosis of MPN by the WHO. High-resolution melt (HRM) curve analysis is a nongel-based, closed-tube method, in which PCR amplification and subsequent analysis are sequentially performed in the well, making it more convenient than other scanning methodologies.
Methods: We evaluated JAK2 V617F mutation by HRM. Twenty-nine patients diagnosed with MPN were examined. We studied the analytical sensitivity of the HRM analysis using real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for identifying the JAK2 V617F mutation. Additionally, the sensitivity of HRM analysis and allele-specific PCR (AS-PCR) assay was compared.
Results: The JAK2 V617F mutation was successfully discriminated at an abundance of 6% or above in HRM analysis. Both HRM analysis and AS-PCR showed 100% accuracy with detection limits of 6% and 2.5%, respectively.
Conclusion: HRM analysis is a fast, simple, reliable, and nonexpensive method for the detection of the JAK2 V617F mutation. However, more validation of the detection limits of HRM analysis should be performed before declaration of the analytic sensitivity of the method.
Keywords: JAK2; high-resolution melt curve; myeloproliferative neoplasm.
© 2016 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapid detection of JAK2 V617F mutation using high-resolution melting analysis with LightScanner platform.Clin Chim Acta. 2010 Dec 14;411(23-24):2097-100. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2010.08.020. Epub 2010 Aug 19. Clin Chim Acta. 2010. PMID: 20728437
-
Detection of the JAK2 V617F missense mutation by high resolution melting analysis and its validation.Clin Chim Acta. 2009 Oct;408(1-2):39-44. doi: 10.1016/j.cca.2009.07.002. Epub 2009 Jul 10. Clin Chim Acta. 2009. PMID: 19595684
-
Accurate quantitation of JAK2 V617F allele burden by array-based digital PCR.Int J Lab Hematol. 2015 Apr;37(2):217-24. doi: 10.1111/ijlh.12269. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Int J Lab Hematol. 2015. PMID: 24963593
-
The V617F JAK2 mutation and the myeloproliferative disorders.Hematol Oncol. 2005 Sep-Dec;23(3-4):91-3. doi: 10.1002/hon.761. Hematol Oncol. 2005. PMID: 16285006 Review.
-
Changing concepts of diagnostic criteria of myeloproliferative disorders and the molecular etiology and classification of myeloproliferative neoplasms: from Dameshek 1950 to Vainchenker 2005 and beyond.Acta Haematol. 2015;133(1):36-51. doi: 10.1159/000358580. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Acta Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25116092 Review.
Cited by
-
Analysis of the reannealing- instead of melting-curve in the detection of JAK2 V617F mutation by HRM method.J Blood Med. 2019 Jul 22;10:235-241. doi: 10.2147/JBM.S204222. eCollection 2019. J Blood Med. 2019. PMID: 31413649 Free PMC article.
-
Oncogenic and tumor suppressor genes expression in myeloproliferative neoplasms: The hidden side of a complex pathology.J Clin Lab Anal. 2022 Apr;36(4):e24289. doi: 10.1002/jcla.24289. Epub 2022 Feb 17. J Clin Lab Anal. 2022. PMID: 35176183 Free PMC article.
-
Development of a high resolution melting analysis assay for rapid identification of JAK2 V617F missense mutation and its validation.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2019 Apr 30;8:10. doi: 10.1186/s40164-019-0134-0. eCollection 2019. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31165012 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Komura E, Chagraoui H, Mansat de Mas V, et al. Spontaneous STAT5 activation induces growth factor independence in idiopathic myelofibrosis: Possible relationship with FKBP51 overexpression. Exp Hematol 2003;31(7):622–630. doi:S0301472X03000857 [pii]. - PubMed
-
- James C, Ugo V, Le Couedic JP, et al. A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signalling causes polycythaemia vera. Nature 2005;434(7037):1144–1148. doi:nature03546 [pii]10.1038/nature03546. - PubMed
-
- Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, et al. Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 2005;365(9464):1054–1061. doi:S0140‐6736(05)71142‐9 [pii]10.1016/S0140‐6736(05)71142‐9. - PubMed
-
- Tefferi A, Thiele J, Orazi A, et al. Proposals and rationale for revision of the World Health Organization diagnostic criteria for polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia, and primary myelofibrosis: Recommendations from an ad hoc international expert panel. Blood 2007;110(4):1092–1097. doi:blood‐2007‐04‐083501 [pii]10.1182/blood‐2007‐04‐083501. - PubMed
-
- Greiner TC. Diagnostic assays for the JAK2 V617F mutation in chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125(5):651–653. doi:NXXTGRCXD0TMA3C2 [pii]10.1309/NXXT‐GRCX‐D0TM‐A3C2. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

