Impact of maternal cigarette smoke exposure on brain inflammation and oxidative stress in male mice offspring
- PMID: 27169932
- PMCID: PMC4864383
- DOI: 10.1038/srep25881
Impact of maternal cigarette smoke exposure on brain inflammation and oxidative stress in male mice offspring
Abstract
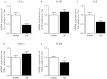
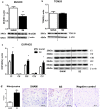
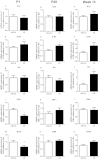
Maternal cigarette smoke exposure (SE) during gestation can cause lifelong adverse effects in the offspring's brain. Several factors may contribute including inflammation, oxidative stress and hypoxia, whose changes in the developing brain are unknown. Female Balb/c mice were exposed to cigarette smoke prior to mating, during gestation and lactation. Male offspring were studied at postnatal day (P) 1, P20 and 13 weeks (W13). SE dams had reduced inflammatory mediators (IL-1β, IL-6 and toll like receptor (TLR)4 mRNA), antioxidant (manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD)), and increased mitochondrial activities (OXPHOS-I, III and V) and protein damage marker nitrotyrosine. Brain hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)1α and its upstream signalling molecule early growth response factor (EGR)1 were not changed in the SE dams. In the SE offspring, brain IL-1R, IL-6 and TLR4 mRNA were increased at W13. The translocase of outer mitochondrial membrane, and MnSOD were reduced at W13 with higher nitrotyrosine staining. HIF-1α was also increased at W13, although EGR1 was only reduced at P1. In conclusion, maternal SE increased markers of hypoxia and oxidative stress with mitochondrial dysfunction and cell damage in both dams and offspring, and upregulated inflammatory markers in offspring, which may render SE dams and their offspring vulnerable to additional brain insults.
Figures



Similar articles
-
A Mitochondrial Specific Antioxidant Reverses Metabolic Dysfunction and Fatty Liver Induced by Maternal Cigarette Smoke in Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 21;11(7):1669. doi: 10.3390/nu11071669. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31330878 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of long-term maternal smoking on the offspring's lung health.Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017 Aug 1;313(2):L416-L423. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00134.2017. Epub 2017 May 18. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2017. PMID: 28522560
-
Impact of maternal cigarette smoke exposure on brain and kidney health outcomes in female offspring.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Dec;43(12):1168-1176. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12659. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27561128
-
Modulation of neural regulators of energy homeostasis, and of inflammation, in the pups of mice exposed to e-cigarettes.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Sep 25;684:61-66. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.07.001. Epub 2018 Jul 4. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29981356
-
Maternal L-carnitine supplementation ameliorates renal underdevelopment and epigenetic changes in male mice offspring due to maternal smoking.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019 Feb;46(2):183-193. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.13038. Epub 2018 Nov 22. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30290012
Cited by
-
Impact of Maternal Environment and Inflammation on Fetal Neurodevelopment.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 11;13(4):453. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040453. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671901 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rhoifolin as a potential anxiolytic drug for the effects of nicotine withdrawal: beneficial effects on behavior, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress.Metab Brain Dis. 2025 May 20;40(5):208. doi: 10.1007/s11011-025-01627-5. Metab Brain Dis. 2025. PMID: 40392377
-
A Mitochondrial Specific Antioxidant Reverses Metabolic Dysfunction and Fatty Liver Induced by Maternal Cigarette Smoke in Mice.Nutrients. 2019 Jul 21;11(7):1669. doi: 10.3390/nu11071669. Nutrients. 2019. PMID: 31330878 Free PMC article.
-
L-Carnitine and extendin-4 improve outcomes following moderate brain contusion injury.Sci Rep. 2018 Jul 25;8(1):11201. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-29430-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30046063 Free PMC article.
-
The role of monocytes in thrombotic diseases: a review.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jun 2;10:1113827. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1113827. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 37332592 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Global status report on noncommunicable disease. Description of the global burden of NCDs, their risk factors and determinants. (2011) (Date of access: 01/04/2011). Available at http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789240686458_eng.pdf?ua=1.
-
- World Health Organisation. World health Organisation report on the Glocal tobacco Epidemic, 2011: Warning about the Dangers of Tobacco. (2011) (Date of access: 07/07/2011). Available at http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2011/9789240687813_eng.pdf?ua=1.
-
- Ng S. P. & Zelikoff J. T. Smoking during pregnancy: Subsequent effects on offspring immune competence and disease vulnerability in later life. Reprod Toxicol. 23, 428–437 (2007). - PubMed
-
- Ng S. P. & Zelikoff J. T. Smoking during pregnancy: subsequent effects on offspring immune competence and disease vulnerability in later life. Reprod Toxicol. 23, 428–437 (2007). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

