LRRK2 phosphorylation level correlates with abnormal motor behaviour in an experimental model of levodopa-induced dyskinesias
- PMID: 27169991
- PMCID: PMC4866295
- DOI: 10.1186/s13041-016-0234-2
LRRK2 phosphorylation level correlates with abnormal motor behaviour in an experimental model of levodopa-induced dyskinesias
Abstract
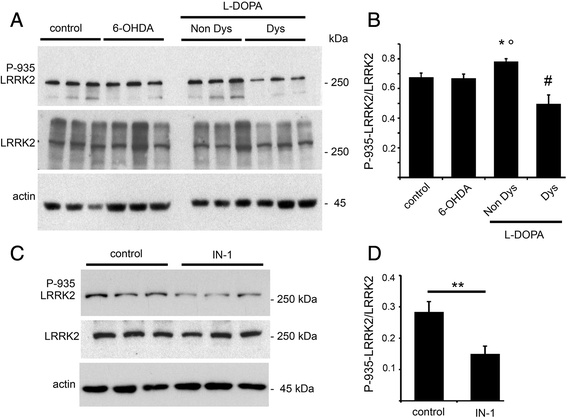
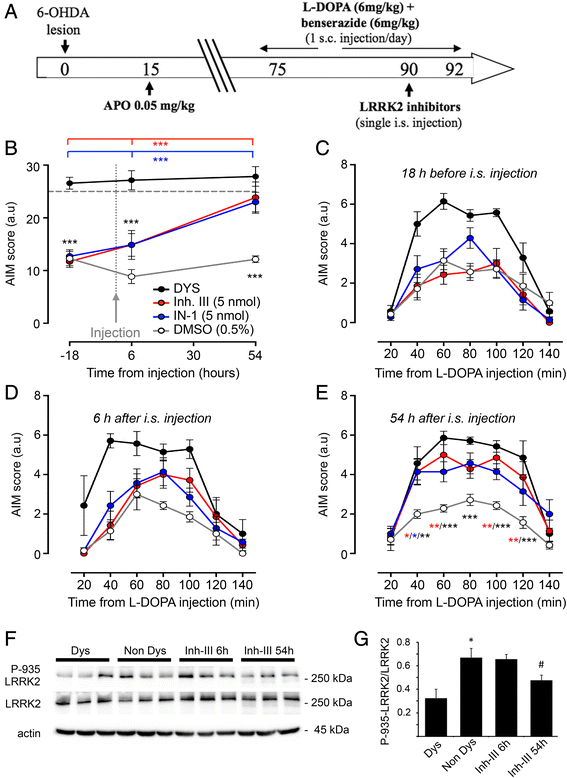
Levodopa (L-DOPA)-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) represent the major side effect in Parkinson's disease (PD) therapy. Leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) mutations account for up to 13 % of familial cases of PD. LRRK2 N-terminal domain encompasses several serine residues that undergo phosphorylation influencing LRRK2 function. This work aims at investigating whether LRRK2 phosphorylation/function may be involved in the molecular pathways downstream D1 dopamine receptor leading to LIDs. Here we show that LRRK2 phosphorylation level at serine 935 correlates with LIDs induction and that inhibition of LRRK2 induces a significant increase in the dyskinetic score in L-DOPA treated parkinsonian animals. Our findings support a close link between LRKK2 functional state and L-DOPA-induced abnormal motor behaviour and highlight that LRRK2 phosphorylation level may be implicated in LIDs, calling for novel therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: 6-OHDA; L-DOPA; L-DOPA-induced dyskinesias; LRRK2; Parkinson’s disease; Phosphorylation; Rat.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

