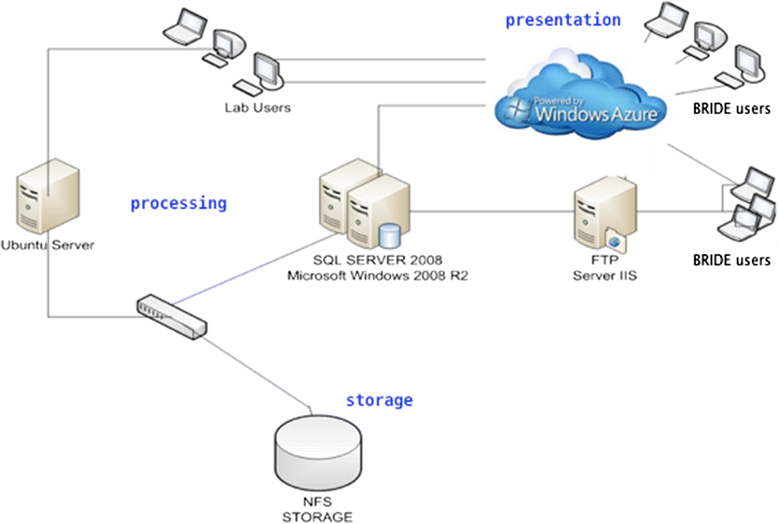
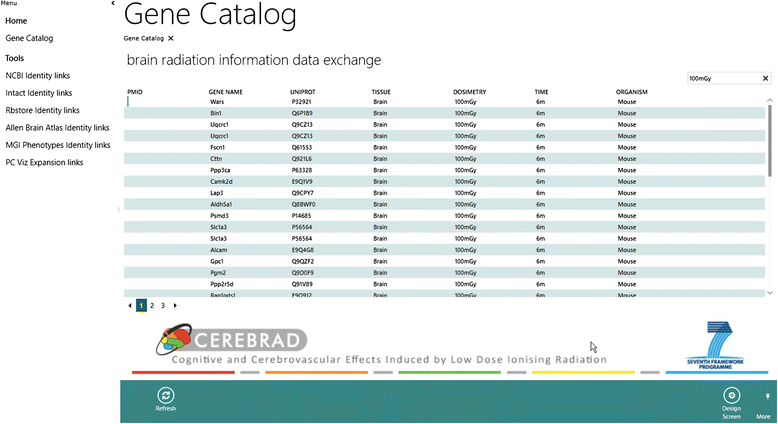
Brain Radiation Information Data Exchange (BRIDE): integration of experimental data from low-dose ionising radiation research for pathway discovery
- PMID: 27170263
- PMCID: PMC4865096
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-016-1068-8
Brain Radiation Information Data Exchange (BRIDE): integration of experimental data from low-dose ionising radiation research for pathway discovery
Abstract
Background: The underlying molecular processes representing stress responses to low-dose ionising radiation (LDIR) in mammals are just beginning to be understood. In particular, LDIR effects on the brain and their possible association with neurodegenerative disease are currently being explored using omics technologies.
Results: We describe a light-weight approach for the storage, analysis and distribution of relevant LDIR omics datasets. The data integration platform, called BRIDE, contains information from the literature as well as experimental information from transcriptomics and proteomics studies. It deploys a hybrid, distributed solution using both local storage and cloud technology.
Conclusions: BRIDE can act as a knowledge broker for LDIR researchers, to facilitate molecular research on the systems biology of LDIR response in mammals. Its flexible design can capture a range of experimental information for genomics, epigenomics, transcriptomics, and proteomics. The data collection is available at: <bride.azurewebsites.net>.
Keywords: Brain research; Data integration; Low-dose ionising radiation; Omics technologies; Systems biology.
Figures
References
-
- De Angelis G, Caldora M, Santaquilani M, Scipione R, Verdecchia A. Radiation exposure of civilian airline crew members and associated biological effects due to the atmospheric ionizing radiation environment. Phys Med. 2001;17(Suppl 1):258–260. - PubMed
-
- Ginzburg HM, Reis E. Consequences of the Nuclear Power Plant Accident at Chernobyl. In: US Department of Energy; 1987. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1580196/pdf/pubhealthrep1500.... - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources