Development of Novel Non-Contact Electrodes for Mobile Electrocardiogram Monitoring System
- PMID: 27170853
- PMCID: PMC4839303
- DOI: 10.1109/JTEHM.2013.2253598
Development of Novel Non-Contact Electrodes for Mobile Electrocardiogram Monitoring System
Abstract
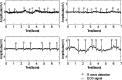
Real-time monitoring of cardiac health is helpful for patients with cardiovascular disease. Many telemedicine systems based on ubiquitous computing and communication techniques have been proposed for monitoring the user's electrocardiogram (ECG) anywhere and anytime. Usually, wet electrodes are used in these telemedicine systems. However, wet electrodes require conduction gels and skin preparation that can be inconvenient and uncomfortable for users. In order to overcome this issue, a new non-contact electrode circuit was proposed and applied in developing a mobile electrocardiogram monitoring system. The proposed non-contact electrode can measure bio-potentials across thin clothing, allowing it to be embedded in a user's normal clothing to monitor ECG in daily life. We attempted to simplify the design of these non-contact electrodes to reduce power consumption while continuing to provide good signal quality. The electrical specifications and the performance of monitoring arrhythmia in clinical settings were also validated to investigate the reliability of the proposed design. Experimental results show that the proposed non-contact electrode provides good signal quality for measuring ECG across thin clothes.
Keywords: Arrhythmia; electrocardiogram (ECG); mobile electrocardiogram monitoring system; non-contact electrode; telemedicine.
Figures








References
-
- Lin Y. H., Jan I. C., Ko P. C. I., Chen Y. Y., Wong J. M., and Jan G. J., “A wireless PDA-based physiological monitoring system for patient transport,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed., vol. 8, no. 4, pp. 439–447, Dec. 2004. - PubMed
-
- Kafeza E., Chiu D. K. W., Cheung S. C., and Kafeza M., “Alerts in mobile healthcare applications: Requirements and pilot study,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed., vol. 8, no. 2, pp. 173–181, Jun. 2004. - PubMed
-
- Lin B. S., Lin B. S., Chou N. K., Chong F. C., and Chen S. J., “RTWPMS: A real-time wireless physiological monitoring system,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed., vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 647–656, Oct. 2006. - PubMed
-
- Rasid M. F. A. and Woodward B., “Bluetooth telemedicine processor for multi-channel biomedical signal transmission via mobile cellular networks,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed., vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 35–43, Mar. 2005. - PubMed
-
- Lee R. G., Chen K. C., Hsiao C. C., and Tseng C. L., “A mobile care system with alert mechanism,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed., vol. 11, no. 5, pp. 507–517, Sep. 2007. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

