Automated Health Alerts Using In-Home Sensor Data for Embedded Health Assessment
- PMID: 27170900
- PMCID: PMC4848095
- DOI: 10.1109/JTEHM.2015.2421499
Automated Health Alerts Using In-Home Sensor Data for Embedded Health Assessment
Abstract
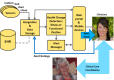
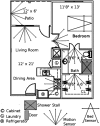
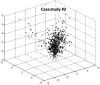
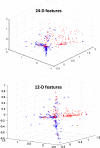
We present an example of unobtrusive, continuous monitoring in the home for the purpose of assessing early health changes. Sensors embedded in the environment capture behavior and activity patterns. Changes in patterns are detected as potential signs of changing health. We first present results of a preliminary study investigating 22 features extracted from in-home sensor data. A 1-D alert algorithm was then implemented to generate health alerts to clinicians in a senior housing facility. Clinicians analyze each alert and provide a rating on the clinical relevance. These ratings are then used as ground truth for training and testing classifiers. Here, we present the methodology for four classification approaches that fuse multisensor data. Results are shown using embedded sensor data and health alert ratings collected on 21 seniors over nine months. The best results show similar performance for two techniques, where one approach uses only domain knowledge and the second uses supervised learning for training. Finally, we propose a health change detection model based on these results and clinical expertise. The system of in-home sensors and algorithms for automated health alerts provides a method for detecting health problems very early so that early treatment is possible. This method of passive in-home sensing alleviates compliance issues.
Keywords: Behavioral bio-markers; eldercare monitoring; health alerts; in-home sensing.
Figures

References
-
- Boockvar K. S. and Lachs M. S., “Predictive value of nonspecific symptoms for acute illness in nursing home residents,” J. Amer. Geriatrics Soc., vol. 51, no. , pp. 1111–1115, 2003. - PubMed
-
- Virone G., et al. , “Behavioral patterns of older adults in assisted living,” IEEE Trans. Inf. Technol. Biomed., vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 387–398, May 2008. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

