Low Voltage Electric Current Causing Ileal Perforation: A Rare Injury
- PMID: 27170922
- PMCID: PMC4852060
Low Voltage Electric Current Causing Ileal Perforation: A Rare Injury
Abstract
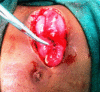
Post-electric burn ileal perforation is a rare but severe complication leading to high morbidity and mortality if there is delay in diagnosis and management. We are describing a case of electric current injury of left forearm, chest, and abdominal wall with perforation of ileum in an 8-year old boy. Patient was successfully managed by primary closure of the ileal perforation.
Keywords: Children; Electric burn; Perforation; Peritonitis.
Figures
References
-
- Lees VC, Frame FD. Electrical burns. In: Settel JA, editor. Principle and Practice of Burn Management. New York: Churchill Livingstone 1996;369-76.
-
- Czuczman AD, Zane RD. Electrical injuries: A review for the emergency clinician. EB Med. 2009;11:1-24.
-
- Behera C, Dr. Rautji R, Dogra TD. Fatal gastro-duodenal perforation following electrocution - a case report. J Indian Acad Forensic Med. 2010;32:248.
-
- Lee RC. Injury by electrical forces: pathophysiology, manifestations and therapy. Curr Probl Surg. 1997;34:677-764. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources