Trends in the Prevalence of Morbid and Severe Obesity in Australian Children Aged 7-15 Years, 1985-2012
- PMID: 27171503
- PMCID: PMC4865229
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0154879
Trends in the Prevalence of Morbid and Severe Obesity in Australian Children Aged 7-15 Years, 1985-2012
Abstract
Objective: Children with severe obesity have greater risk of adverse health outcomes. The purpose of this study was to assess trends in the prevalence of morbid and severe obesity in Australian children between 1985 and 2012.
Methods: Secondary analysis of four national Australian cross-sectional surveys of measured height/weight in 7-15 year olds: Australian Health and Fitness Survey 1985 (n = 8,486), National Nutrition Survey 1995 (n = 1,541), the National Children's Nutrition and Physical Activity Survey 2007 (n = 2,585) and the National Health Survey 2012 (n = 2,940). International Obesity Taskforce cut-point was used for morbid obesity (equivalent to a BMI ≥35kg/m2 at age 18 years). Severe obesity class 2 was defined as BMI ≥120% and <140% of the 95th percentile of the CDC 2000 growth charts or a BMI ≥35 and <40, and severe obesity class 3 as BMI ≥140% of the 95th percentile or a BMI ≥40.
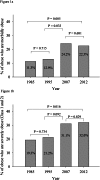
Results: Between 1985 and 2012 the prevalence of morbid obesity increased from 0.2% to 1.8%, class 2 severe obesity from 0.3% to 2.0%, and class 3 from 0.1% to 0.5%. Children with morbid obesity represented 11.3% of children with obesity in 1985 and increased to 22.5% in 2012 (P = 0.005). Children with severe obesity represented 19.3% of children with obesity in 1985 and increased to 32.0% in 2012 (P = 0.016). The greatest increase was observed between 1995 and 2007. The proportion of children who were classified as morbidly or severely obese was not significantly different between 2007 and 2012, nor was it significantly different between age and sex groups.
Conclusion: Prevalence of morbid and severe obesity among children is low, but has significantly increased between 1985 and 2012. In contrast to overweight and obese children, children with morbid obesity require tertiary intervention. Failure to treat these children will have significant implications for the individual child and community.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Rokholm B, Baker JL, Sorensen TI. The levelling off of the obesity epidemic since the year 1999 –a review of evidence and perspectives. Obes Rev. 2010;1: 835–846. - PubMed
-
- Kelly AS, Barlow SE, Rao G, Inge TH, Hayman LL, Steinberger J, et al. Severe obesity in children and adolescents: identification, associated health risks, and treatment approaches: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;128: 1689–1712. 10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182a5cfb3 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pyke JE. Australian health and fitness survey 1985. Parkside SA: The Australian Council for Health and Physical Education and Recreation Inc, 1987.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

