Preclinical Studies of a Kidney Safe Iodinated Contrast Agent
- PMID: 27171830
- PMCID: PMC5084786
- DOI: 10.1111/jon.12356
Preclinical Studies of a Kidney Safe Iodinated Contrast Agent
Abstract
Background and purpose: Contrast-induced acute kidney injury (CI-AKI) is a serious complication of the use of iodinated contrast agents. This problem is particularly acute in interventional neurology and interventional cardiology, probably due to the intra-arterial route of injection, high contrast volumes, and preexisting risk factors of these patients. In an attempt to develop a contrast agent that is less damaging to the kidneys, we have studied the effects of adding a small amount of the substituted cyclodextrin, sulfobutyl-ether-β-cyclodextrin (SBECD), to iohexol in rodent models of renal toxicity.
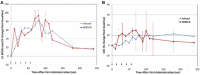
Methods: Renally compromised mice and rats were injected with iohexol and iohexol-SBECD via the tail vein. The renal pathology, creatinine clearance, and survival benefits of iohexol-SBECD were studied. The safety of direct intra-arterial injection of the iohexol-SBECD formulation was studied in a dog heart model system. Mechanism of action studies in cell culture model using a human kidney cell line was performed using flow cytometry.
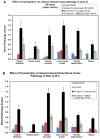
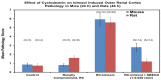
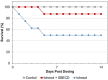
Results: Nephrotoxicity was significantly reduced using iohexol-SBECD compared to iohexol alone, at mole ratios of iohexol:SBECD of 1:0.025. SBECD increased survival from 50% to 88% in a rat survival study. In the dog heart model, iohexol-SBECD was safe. Cell culture studies suggest that SBECD interferes with the early stages of contrast-induced apoptosis in a human renal cell line.
Conclusion: We have shown that the addition of a small amount of SBECD (one molecule of SBECD per 40 iohexol molecules) significantly protects rodent kidneys from CI-AKI. Further development of this new formulation of iodinated contrast is warranted.
Keywords: Contrast renal toxicity; acute kidney injury; iodinated contrast safety; kidney protection from contrast; safe contrast for interventional procedures.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Neuroimaging published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc. on behalf of American Society of Neuroimaging.
Figures





References
-
- Chalikias G, Drosos I, Tziakas DN. Contrast‐induced acute kidney injury: An update. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 2016;30:215‐28. - PubMed
-
- Rihal CS, Textor SC, Grill DE, et al. Incidence and prognostic importance of acute renal failure after percutaneous coronary intervention. Circulation 2002;105:2259‐64. - PubMed
-
- McCullough P. Outcomes of contrast‐induced nephropathy: experience in patients undergoing cardiovascular intervention. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv 2006;67:335‐43. - PubMed
-
- Saeed F, Adil MM, Piracha BH, et al. Acute renal failure worsens in‐hospital outcomes in patients with intracerebral hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 2015;24:789‐94. - PubMed
-
- Qureshi AI. Textbook of Interventional Neurology. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK, 2011.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

