Deciphering the epitranscriptome: A green perspective
- PMID: 27172004
- PMCID: PMC5094531
- DOI: 10.1111/jipb.12483
Deciphering the epitranscriptome: A green perspective
Abstract
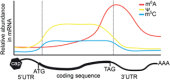
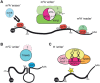
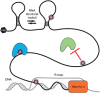
The advent of high-throughput sequencing technologies coupled with new detection methods of RNA modifications has enabled investigation of a new layer of gene regulation - the epitranscriptome. With over 100 known RNA modifications, understanding the repertoire of RNA modifications is a huge undertaking. This review summarizes what is known about RNA modifications with an emphasis on discoveries in plants. RNA ribose modifications, base methylations and pseudouridylation are required for normal development in Arabidopsis, as mutations in the enzymes modifying them have diverse effects on plant development and stress responses. These modifications can regulate RNA structure, turnover and translation. Transfer RNA and ribosomal RNA modifications have been mapped extensively and their functions investigated in many organisms, including plants. Recent work exploring the locations, functions and targeting of N6 -methyladenosine (m6 A), 5-methylcytosine (m5 C), pseudouridine (Ψ), and additional modifications in mRNAs and ncRNAs are highlighted, as well as those previously known on tRNAs and rRNAs. Many questions remain as to the exact mechanisms of targeting and functions of specific modified sites and whether these modifications have distinct functions in the different classes of RNAs.
Keywords: Arabidopsis; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); Pseudouridine (Ψ); RNA 5-methylcytosine (m5C); RNA modifications; epitranscriptome.
© 2016 The Authors. Journal of Integrative Plant Biology Published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Institute of Botany, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Aas PA, Otterlei M, Falnes PO, Vagbo CB, Skorpen F, Akbari M, Sundheim O, Bjoras M, Slupphaug G, Seeberg E, Krokan HE ( 2003) Human and bacterial oxidative demethylases repair alkylation damage in both RNA and DNA. Nature 421: 859–863 - PubMed
-
- Abbasi‐Moheb L, Mertel S, Gonsior M, Nouri‐Vahid L, Kahrizi K, Cirak S, Wieczorek D, Motazacker MM, Esmaeeli‐Nieh S, Cremer K, Weissmann R, Tzschach A, Garshasbi M, Abedini SS, Najmabadi H, Ropers HH, Sigrist SJ, Kuss AW ( 2012) Mutations in NSUN2 cause autosomal‐recessive intellectual disability. Am J Hum Genet 90: 847–855 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Abbasi N, Kim HB, Park NI, Kim HS, Kim YK, Park YI, Choi SB ( 2010) APUM23, a nucleolar Puf domain protein, is involved in pre‐ribosomal RNA processing and normal growth patterning in Arabidopsis . Plant J 64: 960–976 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

