YAP and TAZ in epithelial stem cells: A sensor for cell polarity, mechanical forces and tissue damage
- PMID: 27173018
- PMCID: PMC5031209
- DOI: 10.1002/bies.201600037
YAP and TAZ in epithelial stem cells: A sensor for cell polarity, mechanical forces and tissue damage
Abstract
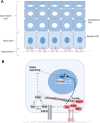
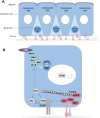
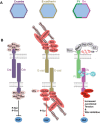
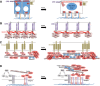
The YAP/TAZ family of transcriptional co-activators drives cell proliferation in epithelial tissues and cancers. Yet, how YAP and TAZ are physiologically regulated remains unclear. Here we review recent reports that YAP and TAZ act primarily as sensors of epithelial cell polarity, being inhibited when cells differentiate an apical membrane domain, and being activated when cells contact the extracellular matrix via their basal membrane domain. Apical signalling occurs via the canonical Crumbs/CRB-Hippo/MST-Warts/LATS kinase cascade to phosphorylate and inhibit YAP/TAZ. Basal signalling occurs via Integrins and Src family kinases to phosphorylate and activate YAP/TAZ. Thus, YAP/TAZ is localised to the nucleus in basal stem/progenitor cells and cytoplasm in differentiated squamous cells or columnar cells. In addition, other signals such as mechanical forces, tissue damage and possibly receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) can influence MST-LATS or Src family kinase activity to modulate YAP/TAZ activity.
Keywords: Hippo pathway; TAZ; YAP; epithelial polarity; mechanosensing; mechanotransduction; wound healing.
© 2016 The Authors BioEssays Published by WILEY Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evolution of mechanotransduction via YAP/TAZ in animal epithelia.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;51:117-123. doi: 10.1016/j.ceb.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29477107 Review.
-
Integrin signalling regulates YAP and TAZ to control skin homeostasis.Development. 2016 May 15;143(10):1674-87. doi: 10.1242/dev.133728. Epub 2016 Mar 17. Development. 2016. PMID: 26989177 Free PMC article.
-
Yap/Taz-TEAD activity links mechanical cues to progenitor cell behavior during zebrafish hindbrain segmentation.Development. 2019 Jul 22;146(14):dev176735. doi: 10.1242/dev.176735. Development. 2019. PMID: 31273051
-
The Hippo pathway integrates PI3K-Akt signals with mechanical and polarity cues to control tissue growth.PLoS Biol. 2019 Oct 15;17(10):e3000509. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.3000509. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Biol. 2019. PMID: 31613895 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of YAP/TAZ Activity by Mechanical Cues: An Experimental Overview.Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1893:183-202. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8910-2_15. Methods Mol Biol. 2019. PMID: 30565135 Review.
Cited by
-
Novel Animal Model of Crumbs-Dependent Progressive Retinal Degeneration That Targets Specific Cone Subtypes.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018 Jan 1;59(1):505-518. doi: 10.1167/iovs.17-22572. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29368007 Free PMC article.
-
A dual role of YAP in driving TGFβ-mediated endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition.J Cell Sci. 2021 Aug 1;134(15):jcs251371. doi: 10.1242/jcs.251371. Epub 2021 Aug 2. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34338295 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear exclusion of YAP exacerbates podocyte apoptosis and disease progression in Adriamycin-induced focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.Lab Invest. 2021 Feb;101(2):258-270. doi: 10.1038/s41374-020-00503-3. Epub 2020 Nov 17. Lab Invest. 2021. PMID: 33203894 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Inactivation of Mst1 and Mst2 in the Mouse Adrenal Cortex.J Endocr Soc. 2022 Sep 16;7(1):bvac143. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvac143. eCollection 2022 Nov 17. J Endocr Soc. 2022. PMID: 36405866 Free PMC article.
-
Drosophila Big bang regulates the apical cytocortex and wing growth through junctional tension.J Cell Biol. 2018 Mar 5;217(3):1033-1045. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201705104. Epub 2018 Jan 11. J Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29326288 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

