Inherent ER stress in pancreatic islet β cells causes self-recognition by autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes
- PMID: 27173406
- PMCID: PMC4958612
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaut.2016.04.009
Inherent ER stress in pancreatic islet β cells causes self-recognition by autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes
Abstract
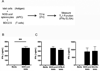
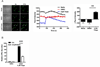
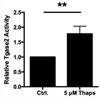
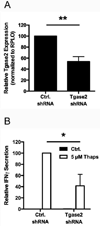
Type 1 diabetes (T1D) is an autoimmune disease characterized by pancreatic β cell destruction induced by islet reactive T cells that have escaped central tolerance. Many physiological and environmental triggers associated with T1D result in β cell endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and dysfunction, increasing the potential for abnormal post-translational modification (PTM) of proteins. We hypothesized that β cell ER stress induced by environmental and physiological conditions generates abnormally-modified proteins for the T1D autoimmune response. To test this hypothesis we exposed the murine CD4(+) diabetogenic BDC2.5 T cell clone to murine islets in which ER stress had been induced chemically (Thapsigargin). The BDC2.5 T cell IFNγ response to these cells was significantly increased compared to non-treated islets. This β cell ER stress increased activity of the calcium (Ca(2+))-dependent PTM enzyme tissue transglutaminase 2 (Tgase2), which was necessary for full stress-dependent immunogenicity. Indeed, BDC2.5 T cells responded more strongly to their antigen after its modification by Tgase2. Finally, exposure of non-antigenic murine insulinomas to chemical ER stress in vitro or physiological ER stress in vivo caused increased ER stress and Tgase2 activity, culminating in higher BDC2.5 responses. Thus, β cell ER stress induced by chemical and physiological triggers leads to β cell immunogenicity through Ca(2+)-dependent PTM. These findings elucidate a mechanism of how β cell proteins are modified and become immunogenic, and reveal a novel opportunity for preventing β cell recognition by autoreactive T cells.
Keywords: Autoimmunity; ER stress; Post-translational modification; Type 1 diabetes; β cell.
Copyright © 2016 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
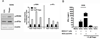

Similar articles
-
Modifying Enzymes Are Elicited by ER Stress, Generating Epitopes That Are Selectively Recognized by CD4+ T Cells in Patients With Type 1 Diabetes.Diabetes. 2018 Jul;67(7):1356-1368. doi: 10.2337/db17-1166. Epub 2018 Apr 13. Diabetes. 2018. PMID: 29654212 Free PMC article.
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates insulin-directed cellular autoimmunity in murine type 1 diabetes.Front Immunol. 2024 Nov 12;15:1474453. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1474453. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39600694 Free PMC article.
-
Changing faces, unmasking the beta-cell: post-translational modification of antigens in type 1 diabetes.Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013 Aug;20(4):299-306. doi: 10.1097/MED.0b013e3283631417. Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2013. PMID: 23770733 Review.
-
Cutting Edge: Nonobese Diabetic Mice Deficient in Chromogranin A Are Protected from Autoimmune Diabetes.J Immunol. 2016 Jan 1;196(1):39-43. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501190. Epub 2015 Nov 25. J Immunol. 2016. PMID: 26608914 Free PMC article.
-
Autoreactive T cells in type 1 diabetes.J Clin Invest. 2017 Aug 1;127(8):2881-2891. doi: 10.1172/JCI94549. Epub 2017 Aug 1. J Clin Invest. 2017. PMID: 28762987 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of β Cell Stress and Neo-Epitopes in the Immunopathology of Type 1 Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Feb 18;11:624590. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2020.624590. eCollection 2020. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 33679609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Setting the Stage for Insulin Granule Dysfunction during Type-1-Diabetes: Is ER Stress the Culprit?Biomedicines. 2022 Oct 25;10(11):2695. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112695. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 36359215 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Distinct secretion pattern of serum proinsulin in different types of diabetes.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Apr;8(7):452. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.189. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32395496 Free PMC article.
-
Neoepitopes in Type 1 Diabetes: Etiological Insights, Biomarkers and Therapeutic Targets.Front Immunol. 2021 Apr 19;12:667989. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.667989. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33953728 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunction and Therapeutic Potential of Endothelial Progenitor Cells in Diabetes Mellitus.J Clin Med Res. 2018 Oct;10(10):752-757. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3581w. Epub 2018 Sep 10. J Clin Med Res. 2018. PMID: 30214646 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Geenen V. Thymus and type 1 diabetes: an update. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2012;98:26–32. - PubMed
-
- Mallone R and van Endert P. T cells in the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes. Curr Diab Rep. 2008;8:101–106. - PubMed
-
- Grupillo M, Gualtierotti G, He J, Sisino G, Bottino R, Rudert WA, Trucco M, Fan Y. Essential roles of insulin expression in Aire+ tolerogenic dendritic cells in maintaining peripheral self-tolerance of islet beta-cells. Cell Immunol. 2012;273:115–123. - PubMed
-
- Wu J, Kaufman RJ. From acute ER stress to physiological roles of the Unfolded Protein Response. Cell Death Differ. 2006;13:374–384. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

