The Effect of Millisecond Pulsed Electric Fields (msPEF) on Intracellular Drug Transport with Negatively Charged Large Nanocarriers Made of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN): In Vitro Study
- PMID: 27173678
- PMCID: PMC5045845
- DOI: 10.1007/s00232-016-9906-1
The Effect of Millisecond Pulsed Electric Fields (msPEF) on Intracellular Drug Transport with Negatively Charged Large Nanocarriers Made of Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLN): In Vitro Study
Abstract
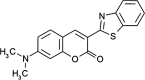
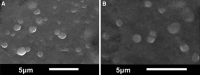
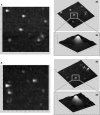
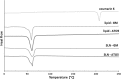
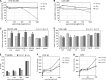
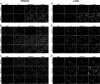
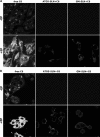
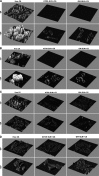
Drug delivery technology is still a dynamically developing field of medicine. The main direction in nanotechnology research (nanocarriers, nanovehicles, etc.) is efficient drug delivery to target cells with simultaneous drug reduction concentration. However, nanotechnology trends in reducing the carrier sizes to several nanometers limit the volume of the loaded substance and may pose a danger of uncontrolled access into the cells. On the other hand, nanoparticles larger than 200 nm in diameter have difficulties to undergo rapid diffusional transport through cell membranes. The main advantage of large nanoparticles is higher drug encapsulation efficiency and the ability to deliver a wider array of drugs. Our present study contributes a new approach with large Tween 80 solid lipid nanoparticles SLN (i.e., hydrodynamic GM-SLN-glycerol monostearate, GM, as the lipid and ATO5-SLNs-glyceryl palmitostearate, ATO5, as the lipid) with diameters DH of 379.4 nm and 547 nm, respectively. They are used as drug carriers alone and in combination with electroporation (EP) induced by millisecond pulsed electric fields. We evaluate if EP can support the transport of large nanocarriers into cells. The study was performed with two cell lines: human colon adenocarcinoma LoVo and hamster ovarian fibroblastoid CHO-K1 with coumarin 6 (C6) as a fluorescent marker for encapsulation. The biological safety of the potential treatment procedure was evaluated with cell viability after their exposure to nanoparticles and EP. The EP efficacy was evaluated by FACS method. The impact on intracellular structure organization of cytoskeleton was visualized by CLSM method with alpha-actin and beta-tubulin. The obtained results indicate low cytotoxicity of both carrier types, free and loaded with C6. The evaluation of cytoskeleton proteins indicated no intracellular structure damage. The intracellular uptake and accumulation show that SLNs do not support transport of C6 coumarin. Only application of electroporation improved the transport of encapsulated and free C6 into both treated cell lines.
Keywords: Coumarin-6; Drug delivery; Electroporation; Millisecond pulsed electric field; Solid lipid nanocarriers.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Curcumin Loaded Nanocarriers with Varying Charges Augmented with Electroporation Designed for Colon Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1377. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031377. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163301 Free PMC article.
-
Electroporation and lipid nanoparticles with cyanine IR-780 and flavonoids as efficient vectors to enhanced drug delivery in colon cancer.Bioelectrochemistry. 2016 Aug;110:19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2016.02.013. Epub 2016 Feb 27. Bioelectrochemistry. 2016. PMID: 26946158
-
Cellular uptake of coumarin-6 as a model drug loaded in solid lipid nanoparticles.J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011 Feb;62(1):45-53. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2011. PMID: 21451209
-
Solid lipid nanocarriers in drug delivery: characterization and design.Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018 Aug;15(8):771-785. doi: 10.1080/17425247.2018.1504018. Expert Opin Drug Deliv. 2018. PMID: 30064267 Review.
-
Drug targeting using solid lipid nanoparticles.Chem Phys Lipids. 2014 Jul;181:56-61. doi: 10.1016/j.chemphyslip.2014.03.006. Epub 2014 Apr 6. Chem Phys Lipids. 2014. PMID: 24717692 Review.
Cited by
-
Curcumin Loaded Nanocarriers with Varying Charges Augmented with Electroporation Designed for Colon Cancer Therapy.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 26;23(3):1377. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031377. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163301 Free PMC article.
-
Benefitial role of electrochemotherapy in locally advanced pancreatic cancer - radiological perspective.Pol J Radiol. 2022 Jan 13;87:e30-e42. doi: 10.5114/pjr.2022.112674. eCollection 2022. Pol J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35140826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanoemulsion Structural Design in Co-Encapsulation of Hybrid Multifunctional Agents: Influence of the Smart PLGA Polymers on the Nanosystem-Enhanced Delivery and Electro-Photodynamic Treatment.Pharmaceutics. 2019 Aug 11;11(8):405. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics11080405. Pharmaceutics. 2019. PMID: 31405247 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aihara H, Miyazaki J. Gene transfer into muscle by electroporation in vivo. Nat Biotechnol. 1998;16(9):867–870. - PubMed
-
- Bazylińska U, Pietkiewicz J, Saczko J, Nattich-Rak M, Rossowska J, Garbiec A, Wilk KA. Nanoemulsion-templated multilayer nanocapsules for cyanine-type photosensitizer delivery to human breast carcinoma cells. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2012;47:406–420. - PubMed
-
- Bazylińska U, Kulbacka J, Wilk KA. Dicephalic ionic surfactants in fabrication of biocompatible nanoemulsions: factors influencing droplet size and stability. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 2014;460:312–320.
-
- Bazylińska U, Pucek A, Sowa M, Matczak-Jon E, Wilk KA. Engineering of phosphatidylcholine-based solid lipid nanocarriers for flavonoids delivery. Colloids Surf A: Physicochem Eng Asp. 2014;460:483–493.
-
- Born SL, Hu JK, Lehman-McKeeman LD. o-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde is a hepatotoxic metabolite of coumarin. Drug Metab Dispos. 2000;28(2):218–223. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

