Viral evasion of intracellular DNA and RNA sensing
- PMID: 27174148
- PMCID: PMC5072394
- DOI: 10.1038/nrmicro.2016.45
Viral evasion of intracellular DNA and RNA sensing
Abstract
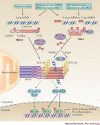
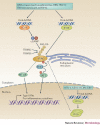
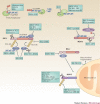
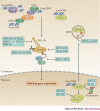
The co-evolution of viruses with their hosts has led to the emergence of viral pathogens that are adept at evading or actively suppressing host immunity. Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) are key components of antiviral immunity that detect conserved molecular features of viral pathogens and initiate signalling that results in the expression of antiviral genes. In this Review, we discuss the strategies that viruses use to escape immune surveillance by key intracellular sensors of viral RNA or DNA, with a focus on RIG-I-like receptors (RLRs), cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS) and interferon-γ (IFNγ)-inducible protein 16 (IFI16). Such viral strategies include the sequestration or modification of viral nucleic acids, interference with specific post-translational modifications of PRRs or their adaptor proteins, the degradation or cleavage of PRRs or their adaptors, and the sequestration or relocalization of PRRs. An understanding of viral immune-evasion mechanisms at the molecular level may guide the development of vaccines and antivirals.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Yoneyama M, et al. The RNA helicase RIG-I has an essential function in double-stranded RNA-induced innate antiviral responses. Nat. Immunol. 2004;5:730–737. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

